Enthalpies for Different Types of Reactions
Enthalpies for Different Types of Reactions: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Enthalpy of Dilution, Lattice Enthalpy, Mean Bond Enthalpy & Ionization Energy and Electron Affinity etc.
Important Questions on Enthalpies for Different Types of Reactions
What is the enthalpy change for,
if heat of formation of are and respectively (in standard conditions)?
The enthalpy change that accompanies melting of one mole of a solid substance in standard state is called enthalpy of atomization.
What is the difference between heat of solution and heat of dilution?
The integral heat of dilution is viewed on a macro scale.
The _____ heat/enthalpy of dilution is viewed on a micro scale.
A gas mixture of of ethylene and methane on complete combustion at and at pressure produce of carbon dioxide. Find out the amount of heat evolved in , during this combustion. and
The lattice enthalpy and hydration enthalpy of four compounds are given below:
| Compounds | Lattice enthalpy | Hydration enthalpy |
| (in ) | (in ) | |
The pair of compounds which is soluble in water is
The amount of energy released in burning of coal is
Match the column I with column II and mark the appropriate choice.
| Column - I | Column - II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Calculatebond enthalpy from the following data:
Calculate of the reaction
from the following data:
What is meant by bond enthalpy? How is it useful to calculate reaction enthalpy? Explain with one example.
Explain standard enthalpy of combustion with an example.
Define and explain enthalpy of atomization with an example.
Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction,
and hence, calculate the bond enthalpy of
bond in from the following data;
where is the enthalpy of atomization.
Calculate, using the data given in the table below, the enthalpy of the reaction,
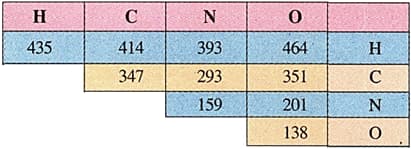
The standard enthalpy of combustion at of hydrogen, cyclohexane and cyclohexane are and respectively. Calculate the heat of hydrogenation of cyclohexane.
Select the incorrect statement(s) from the following:
Given,
What is the standard enthalpy of formation of NH3 gas in KJ mole-1.
One mole of methanol, when burnt in oxygen, gives out 723 kJ heat. If one mole of oxygen is used, what will be the amount of heat evolved?
