Fundamentals of Thermodynamics
Fundamentals of Thermodynamics: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Heat Capacity, Molar Heat Capacity at Constant Volume (Cv), Characteristics of Internal Energy & Sign Conventions for Heat etc.
Important Questions on Fundamentals of Thermodynamics
A piece of metal weighing is heated to and dropped into of cold water in an insulated container at . If the final temperature of the water in the container is , the specific heat of the metal in . is
When equal volumes of Helium and Neon at same temperature and pressure are mixed, the ratio of the mixture equals:
Which energy is a part of mechanical energy?
A heat pump is used to draw water from a well. The temperature of the water is and that of the atmosphere is . If the amount of water drawn is from a depth of , calculate the amount of heat supplied to the well in kJ.
Express your answer up to nearest integer value.
The process in which the value of is:
The quantity of heat (in ) required to raise the temperature of of ethanol from to the boiling point and then change the liquid to vapor at that temperature is closest to [Given, boiling point of ethanol . Specific heat capacity of liquid ethanol . Latent heat of vaporisation of ethanol ]
An ideal monoatomic gas is subjected to following change.
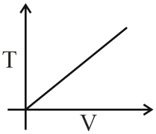
If is the gas constant then the molar heat capacity of the gas for the process is,
If we place Lithium metal in coffee cup calorimeter that already contains of water. The specific heat capacity of reaction mixture is . Temperature of water is increased from to . Then find for the reaction.
The internal energy of an ideal gas is plotted against volume for a cyclic process , as shown in the figure.
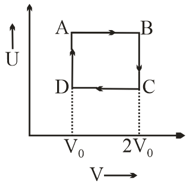
The temperature of the gas at and are and , respectively. The heat absorbed by the gas (in ) in this cyclic process, is :
How much heat will be required at constant volume at to form of from and
Given:
one mole of an ideal gas at is expanded isothermally from an initial volume of to . The for this process is:
An ideal gas initially at temperature with expands adiabatically into vacuum to double its volume. The final temperature is given by:
A water heater, operating on a hydrocarbon fuel heats water flowing at the rate of per minute, from to . If the heat of combustion of hydrocarbon is , how much fuel in is consumed per minute? (Specific heat of water is
A diatomic ideal gas changes its state from to as shown in the figure.
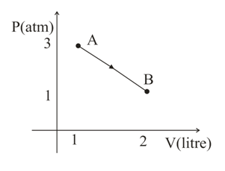
Choose the correct versus graph: (where is internal energy of the gas)
One gram sample of is decomposed in a bomb calorimeter temperature increases by . The heat capacity of the system is . What is the molar heat of decomposition for ?
Which of the following statement is INCORRECT ?
The internal energy of an ideal gas increases during an isothermal process when the gas is :-
A reaction proceeds through two paths and to convert .
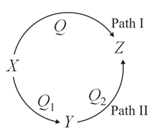
What is the correct relationship between , and ?
The entropy change accompanying the heating of one mole of helium gas, assuming ideal behaviour, from a temperature of to a temperature of at constant pressure, in is ( Give answer to the nearest integer after rounding off.)
of heat is provided to the system. Work done on the system is . What is the change in internal energy?
