Friction
Friction: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Friction, Laws of Friction, Friction Due to Inclined Plane in Downward Motion & Minimum Force to Keep a Body Stationary on a Vertical Wall etc.
Important Questions on Friction
Consider a car moving along a straight horizontal road with speed of . If the coefficient of static friction between the tyres and the road is , the shortest distance in which the car can be stopped is (taking )
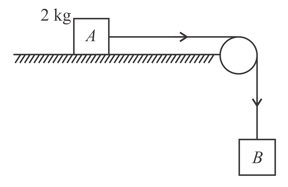
The coefficient of static friction, between block of mass and the table as shown in the figure is . The maximum mass value of block so that the two blocks do not move is (The string and the pulley are assumed to be smooth and massless
A force acts horizontally on a block of placed on a horizontal rough surface of coefficient of friction . If the acceleration due to gravity (g) is taken as the acceleration of the block is
A block of mass is placed on a truck which accelerates with acceleration . The coefficient of static friction between the block and truck is . The frictional force acting on the block is
A person slides freely down a frictionless inclined plane while his bag falls vertically from the same height. The final speeds of the man and the bag should be such that :
A block of mass rests on a rough inclined plane making an angle of with the horizontal. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the plane is The frictional force on the block is
a marble block of mass lying on the ice when given a velocity of is stopped by frictional force in . Then the coefficient of friction is
(take )
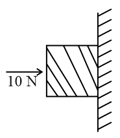
A horizontal force of is necessary to just hold a block stationary against a wall. The coefficient of friction between the block and the wall is . The weight of the block is –
A block rests on a rough inclined plane making an angle of with the horizontal. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the plane is . If the frictional force on the block is , the mass of the block (in ) is (take: ),
A block of mass lies on a horizontal surface in a truck. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the surface is . If the acceleration of the truck is . Find the frictional force acting on the block.
Friction force acting on object is given as function of angle '' then find where will be minimum.
A man walks over a rough surface, the angle between the force of friction and the instantaneous velocity of the person is:
A man walks over a rough surface starting from rest, the angle between the force of friction and the instantaneous velocity of the person is
Find the position coordinates of the image of the object as seen through the periscope. The mirrors are inclined at with -axis and eye is placed at the level .
A block is attached to a horizontal spring of stiffness . The other end of the spring is attached to a fixed wall. The entire system lie on a horizontal surface and the spring is in natural state. The natural length of the spring is . If the block is slowly lifted up vertically to a height from its initial position. which of the following is not correct:
The kind of force that acts between moving surfaces is called _____.
A body of mass moving on a horizontal surface with an initial velocity comes to rest after . If one wants to keep the body moving on the same surface with the same velocity , then the force required is
A test tube containing some water is surrounded by melting ice (pure). Then, the water in the test tube will
