Structure and Properties of Matter - Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other
Structure and Properties of Matter - Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other: Overview
This topic covers various concepts like Pure Substances, , etc.
Important Questions on Structure and Properties of Matter - Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other
Compute the work which must be performed to slowly pump the water out of a hemispherical reservoir of radius
Which of the following are not state functions?
During isothermal expansion of an ideal gas, its
The work done during the expansion of a gas from a volume of against a constant external pressure of 3 atm is (1 L atm = 101.32 J):
For the reaction
When mol of a gas is heated at constant volume, temperature is raised from K. If heat supplied to the gas is J, then which statement is correct?
If is the change in enthalpy and the change in internal energy accompanying a gaseous reaction, then
Mention the factors on which the rate of diffusion of gases depends. Why are similar conditions of temperature and pressure necessary?
How do gases differ from solids and liquids?
Explain the statement 'Gases have neither a fixed shape nor a fixed volume'.
ice at is mixed with steam at . The final temperature of the mixture is.
What is compound?
Why do we need to use a glass rod for stirring any solution and not spoon?
A container is filled with moles of an ideal diatomic gas at absolute temperature When heat is supplied to gas temperature remains constant but moles dissociates into atoms. Heat energy supplied to gas is?
One mole of an ideal gas undergoes two different cyclic processes and , as shown in the diagrams below. In cycle , processes and are isobaric, isothermal, isobaric and isochoric, respectively. In cycle , processes and are isothermal, isochoric, isobaric and isochoric, respectively. The total work done during cycle is and that during cycle is . The ratio is _____.
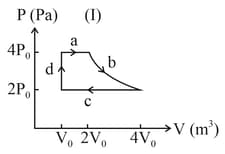
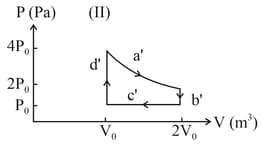
How intermolecular spaces affect the volume?
One mole of an ideal monoatomic gas undergoes two reversible processes and as shown in the given figure:
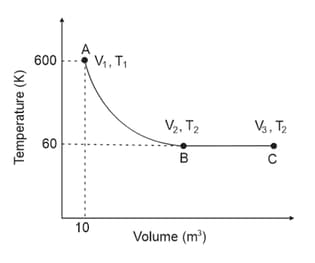
is an adiabatic process. If the total heat absorbed in the entire process and is , the value of is
[Use molar heat capacity of the gas at constant pressure, ]
Calculate the change in internal energy, and enthalphy, when moles of is heated from . The specific heats of at constant pressure and constant volume are and respectively.
For the reaction :
at constant temperature is
For the above reaction the value of is at . The value of in K.cal is____.(Given ).
