Motional Electromotive Force
Motional Electromotive Force: Overview
This topic consists of various concepts like Motional Emf in a Conductor,Fleming's Right Hand Rule for Induced Current,Derivation of Motional Emf, etc.
Important Questions on Motional Electromotive Force
A jet plane is travelling towards wets at a speed of . What is the voltage difference developed between the ends of the wing having a span of , if the Earth’s magnetic field at the location has a magnitude of and the dip angle is ?
Figure shows a rectangular conductor in which the conductor is free to move in a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the paper. The field extends from to and is zero for . Assume that only the arm possesses resistance . When the arm is pulled outward from with constant speed , the joules heating loss from would be:
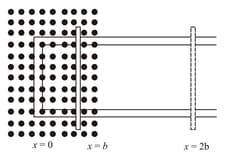
The figure given below shows an arrangement by which current flows through the bulb (X) connected with coil B, when a.c. is passed through coil A.
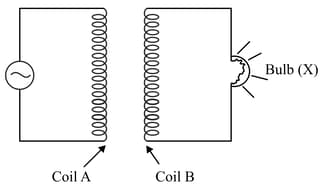
(i) Name the phenomenon involved.
(ii) If a copper sheet is inserted in the gap between the coils, explain how the brightness of the bulb would change.
A conducting rod of length rotates with a uniform angular velocity about its perpendicular bisector. A uniform magnetic field exists parallel to the axis of rotation. The potential difference between the two ends of the rod
A long metallic rod is rotated with about an axis normal to the rod passing through its one end. The other end of the rod is in contact with a circular metallic ring. A constant and uniform magnetic field parallel to the axis exists everywhere. The emf developed between the centre and the ring is _________.
(Take )
A long metal rod completes the circuit as shown in figure. The plane of the circuit is perpendicular to the magnetic field of flux density . If the resistance of the circuit is , the force needed to move the rod in direction, as indicated, with a constant speed of will be _______.
An emf of is induced in a metal rod of length held normal to a uniform magnetic field of , when move with a velocity of:
A conducting rod of length is moved across a magnetic field of , with constant speed of . Find force (in ) on rod.
Direction of magnetic field is inside the plane of the paper as shown in the figure. A moving rod of length has induced EMF of . Find the velocity of the rod.
(Given )
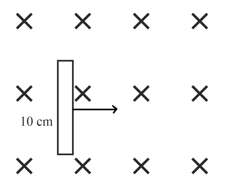
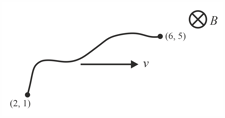
A random shaped conducting wire is moved in a uniform magnetic field as shown. Find motional emf induced across its end at this instant for which its coordinates are mentioned? [ is along -axis]
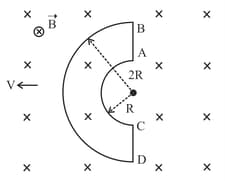
A metallic rod of length is rotated with a frequency of revolution per second, with one end hinged at the centre and the other end at the circumference of a circular metallic ring of radius about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the ring. A constant uniform magnetic field of parallel to the axis is present everywhere. The emf between the centre and the metallic ring is
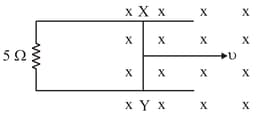
If given arrangement is moving towards left with speed , then potential difference between and and current in the loop are respectively
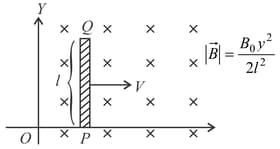
For the conductor , at the instant shown, find .
The spokes of a wheel are made of metal and their lengths are of one metre. On rotating the wheel about its own axis in a uniform magnetic field of tesla normal to the plane of wheel, a potential difference of is generated between the rim and the axis. The rotational velocity of the wheel is
A conducting rod of length is hinged at point . It is free to rotate in vertical plane. There exists a uniform magnetic field in horizontal direction. The rod is released from position shown in the figure. When rod makes an angle from released position then potential difference between two ends of the rod is proportional to:
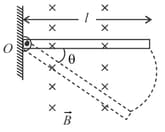
A conductor is bent in -shape and another conductor is sliding with constant velocity directed perpendicular to its length as shown in the figure. The sliding conductor always makes equal angle with the two arms of the bent conductor. If resistance per unit length of each conductor is then current in the loop formed by conductors is,
What is motional emf? State any two factors on which it depends.
State Fleming's right-hand rule.
What is the formula for induced e.m.f. in a coil caused by a change in magnetic flux through the coil if the area of the coil is and the magnetic flux is ?
What do you mean by motional emf?
