Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in Magnetic Field
Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in Magnetic Field: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Force on a Straight Current Wire in Uniform Magnetic Field, Direction of Magnetic Force on a Current Carrying Wire, Force on a Curved Current Wire in Uniform Magnetic Field, etc.
Important Questions on Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in Magnetic Field
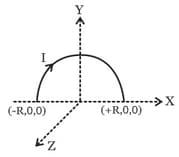
A semi circular current carrying wire having radius is placed in plane with its centre at origin . There is non-uniform magnetic field is existing in the region. The magnetic force acting on semi-circular wire will be along:
Electric charge is uniformly distributed over a rod of length . The rod is placed parallel to a long wire carrying a current . The separation between the rod and the wire is . Find the force needed to move the rod along its length with a uniform velocity .
A parallel plate capacitor is charged by a battery. After some time the battery is disconnected and a dielectric slab of dielectric constant K is inserted between the plates. How would (i) the capacitance, (ii) the electric field between the plates and (iii) the energy stored in the capacitor, be affected?
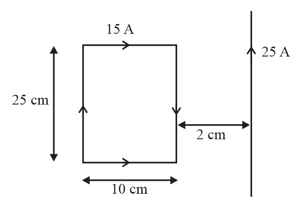
Figure shows a rectangular current-carrying loop placed away from a long, straight, current-carrying conductor. What is the magnitude of the net force acting on the loop in .
A current carrying wire is placed parallel to the lines of force in a magnetic field.
The horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field at a certain place is . It is directed from the geographic south to the geographic north. The force per unit length on a very long straight conductor carrying a steady current of in east-west direction is:
A current of is flowing in a wire of length . A force of acts on it when it is placed in a uniform magnetic field of . The angle between the magnetic field and the direction of the current is:
A metal wire of mass slides without friction on two rails placed at a distance apart. The track lies in a uniform vertical magnetic field. A constant current flows along the rails across the wire and back down the other rail. The acceleration of the wire is
of current is flowing in a linear conductor having a length of . The conductor is placed in a magnetic field of strength and makes an angle of with direction of the field. It experiences a force of magnitude
Two free parallel wires carrying currents in the opposite directions
A horizontal wire of length carries a current of . If the mass of the wire is , the minimum magnetic field required to support the weight of the wire is
Cotyledons are also called-
The magnetic force per unit length on a wire carrying a current of and making an angle of with the direction of a uniform magnetic field of is
The horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field at a certain place is . It is directed from the geographic south to the geographic north. The force per unit length on a very long straight conductor carrying a steady current of in east-west direction is:
A current of is flowing in a wire of length . A force of acts on it when it is placed in a uniform magnetic field of . The angle between the magnetic field and the direction of the current is:
A loop of flexible conducting wire lies in a magnetic field of with its perpendicular to the field. The length of the wire is . When a current of is passed through the loop. It opens into circle, then the tension developed in the wire is
A conducting circular loop of radius carries a constant current . It is placed in a uniform magnetic field , such that is perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The magnetic force acting on the loop is
A conductor of length carrying a current is placed perpendicular to a long straight conductor carrying a current as shown. The force on will be
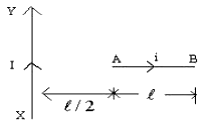
Currents of 10 A , 2 A are passed through two parallel wires A and B respectively in opposite directions. If the wire A is infinetely long and the length of the wire B is 2 metre, the force on the conductor B, which is situated at 10cm distance from A will be
A horizontal wire of length 0.05m carries a current of 5A. If the mass of the wire is 10mg, the minimum magnetic field required to support the weight of the wire is
