Ideal Gas Laws
Ideal Gas Laws: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Gaseous State, Real and Ideal Gas Molecules, Gay-Lussac's Law & Universal Gas Constant etc.
Important Questions on Ideal Gas Laws
of a gas at a pressure of is compressed to . Taking the temperature to remain constant, the increase in pressure, is
Under what conditions will a pure sample of an ideal gas not only exhibit a pressure of but also a concentration of ?
Select one correct statement. In the gas equation, PV = nRT
The volume of air in a car tyre is about at a temperature of and pressure .
Calculate the number of molecules in the tyre( in no. of Molecules).
A container of an ideal gas that is isolated from its surroundings is divided into two parts. One part has double the volume of the other. The pressure in each part is and the temperature is the same. The partition is removed. What is the pressure in the container now?
Which method do we use to separate a mixture of gases having different molecular weights?
The equation of state corresponding to of is,
If the pressure and the volume of certain quantity of ideal gas are halved, then its temperature
The expansion of an ideal gas of mass in volume at constant pressure is given by the straight line. Then the expansion of the same ideal gas of mass at a pressure is given by the straight line
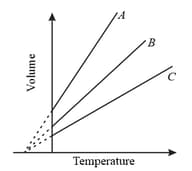
The volume of vessel is twice the volume of another vessel and both of them are filled with the same gas. If the gas in is at twice the temperature and twice the pressure in comparison to the gas in , then the ratio of the gas molecules in to that of is
The temperature of an open room of volume increases from to due to the sunshine. The atmospheric pressure in the room remains . If and are the number of molecules in the room before and after heating, then will be:
Modern vacuum pumps can evacuate a vessel down to a pressure of at room temperature (). Taking , and , the mean distance between molecules of gas in an evacuated vessel will be of the order of:
For the P-V diagram given for an ideal gas
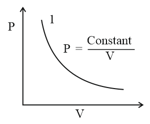
Out of the following which one correctly represents the T-P diagram?
Air is filled in a bottle at atmospheric pressure and it is corked at . If the cork can come out at a pressure times the atmospheric pressure, then up to what temperature should the bottle be heated in order to remove the cork?
Significance of and in Van der Waals equation:
A thermally isolated cylindrical closed vessel of height is kept vertically. It is divided into two equal parts by a diathermic (perfect thermal conductor) frictionless partition of mass Thus the partition is held initially at a distance of from the top, as shown in the schematic figure below. Each of the two parts of the vessel contains mole of an ideal gas at temperature The partition is now released and moves without any gas leaking from one part of the vessel to the other. When equilibrium is reached, the distance of the partition from the top (in ) will be ______ (take the acceleration due to gravity and the universal gas ).
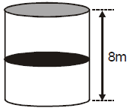
An air bubble of radius is at a depth of below the water surface. Taking atmospheric pressure as Surface tension of water as and density of atmospheric air as the density is of air inside the air bubble, find .
The change in the magnitude of the volume of an ideal gas when a small additional pressure is applied at a constant temperature, is the same as the change when the temperature is reduced by a small quantity at constant pressure. The initial temperature and pressure of the gas were and respectively. If then value of in is ___________ .
Which one is the correct dimensional formula for Boltzmann constant?
