First Law of Thermodynamics
First Law of Thermodynamics: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Isotherm, Sign Convention in Thermodynamics, Equation for Work Done, First Law of Thermodynamics, Work Done by Thermodynamic System, Internal Energy in Thermodynamics, etc.
Important Questions on First Law of Thermodynamics
An ideal monoatomic gas is confined in a horizontal cylinder by a spring loading piston (as shown in Fig ). Initially the gas is at temperature pressure and volume and the spring is in relaxed state. The gas is then Fig. heated very slowly to temperature , pressure and volume . During this process the piston moves out by a distance . Ignoring the friction between the piston and the cylinder, the correct statements is (are)
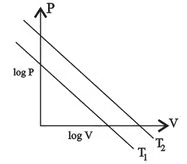
For the following two isotherms drawn at two different temperature and which of the following statement is true? ( number of moles are constant )
An ideal gas at is compressed adiabatically to of its original volume. The rise in temperature is (Take )
Show that slope of adiabatic curve is times the slope of isothermal process.
The slope of isothermal and adiabatic curves are related as
The graph for Boyle's law is called
An ideal gas is allowed to expand freely against vacuum in a rigid insulated container. The gas undergoes
An ideal is filled in a closed, rigid and thermally-insulated container. A coil of resistance and carrying a current of supplies heaT to the gas. The change in the internal energy of the gas after minutes will be:
During an adiabatic expansion, a gas does of work against the surroundings. It is then cooled at constant volume by removing of energy from the gas. The magnitude of the total change in internal energy of the gas is . The value of is
A rigid diatomic ideal gas undergoes an adiabatic process at room temperature. The relation between temperature and volume for this process is constant, then is:
A cycle tyre bursts suddenly. What is the type of this process?
Two identical cylinders and with frictionless pistons contain the same ideal gas at the same temperature and the same volume . The mass of the gas in is and that in is . The gas in each cylinder is now allowed to expand isothermally to the same final volume . The change in the pressure in and are found to be and respectively. Then
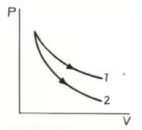
P-V plots for two gases during adiabatic processes are shown in the figure. Plots and should correspond respectively to:
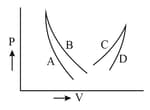
In adjoining diagram, no heat exchange between the gas and the surroundings will take place if the gas is taken along:
One mole of an ideal gas at pressure and temperature volume is expanded isothermally to twice its volume and then compressed at constant pressure to and the gas is brought to its original state by a process in which (Pressure is directly proportional to volume). The correct representation of the process is
One mole of an ideal monatomic gas is taken through a semicircular thermodynamic process shown in the diagram. The heat supplied to the system is
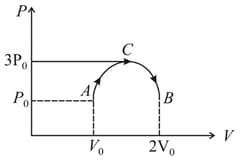
One mole of an ideal gas is taken through the process, as shown in the figure. The temperature of the gas at is .The total work done on the gas is,
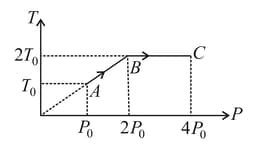
Which one of the following statement is true about a gas undergoing isothermal change?
A given mass of gas at a pressure and absolute temperature obeys the law during an adiabatic process. The adiabatic bulk modulus of the gas at a pressure is
A thermally insulated vessel with nitrogen gas at is moving with a velocity of . If the vessel is stopped suddenly, the percentage change in the pressure of the gas is nearly (Assume entire loss in of the gas is given as heat to gas and )
