Thermal Equilibrium
Thermal Equilibrium: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Adiabatic Boundaries, Diathermic Boundaries & Thermodynamic Equilibrium and Processes etc.
Important Questions on Thermal Equilibrium
Diagram shows a horizontal cylindrical container of length , which is partitioned by a tight-fitting separator. The separator is diathermic but conducts heat very slowly. Initially the separator is in the state shown in the diagram. The temperature of left part of cylinder is and that on right part is . Initially the separator is in equilibrium. As heat is conducted from right to left part, separator displaces to the right. Find the displacement of separator after a long when gases on the two parts of cylinder are in thermal equilibrium.
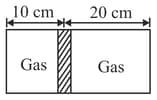
Which of the following is constant in a diathermic boundary?
A diathermic boundary is a boundary that allows_____to transfer.
Which of the following is constant in a diathermic boundary?
A diathermic boundary is a boundary that allows heat to transfer.
All such boundaries of thermodynamic system that are impermeable to the flow of heat across itself are called _____.
Which one of the following is correct about an adiabatic boundary?
Adiabatic refers to a process in which no heat is transferred into or out of a system.
When the temperature of a body is equal to that of the surroundings then the body appears
When the temperature of a body is equal to that of the surroundings then the body appears
At the thermal equilibrium state temperature is constant.
Ice at is added to of water initially at in a vacuum flask. When of ice has been added and has all melted, the temperature of flask and contents is , When a further of ice is added and has all melted, the temperature of the whole becomes . Neglecting heat lost to surroundings the latent heat of fusion of ice is :
The thermo emf E (in volts) of a certain thermocouple is found to vary with Q (in C) according to equation is temperature of the hot function, the cold function being kept at . Then, the neutral temperature of the thermocouple is
