Thermodynamic Processes and Indicator Diagrams
Thermodynamic Processes and Indicator Diagrams: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Equation for Work Done, Internal Energy, Work Done in Adiabatic Process, Reversible and Irreversible Processes, Quasi-static Process, Isotherm, Work Done in Isothermal Process and, Internal Energy in Thermodynamics
Important Questions on Thermodynamic Processes and Indicator Diagrams
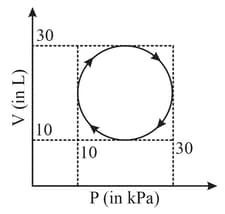
Heat absorbed by a system in going through a cyclic process shown in figure is :
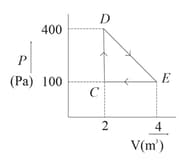
The initial pressure and volume of an ideal gas are and . The final pressure of the gas when the gas is suddenly compressed to volume will be:
(Given = ratio of specific heats at constant pressure and at constant volume.)
A thermodynamic system is taken through cyclic process. The total work done in the process is :
The thermodynamic process, in which internal energy of the system remains constant is
Consider two containers and containing monoatomic gases at the same Pressure , Volume and Temperature . The gas in is compressed isothermally to of its original volume while the gas in is compressed adiabatically to of its original volume. The ratio of final pressure of gas in to that of gas in is
A gas is compressed adiabatically, which one of the following statement is NOT true?
A mixture of gases with adiabatic coefficient equal to is compressed from initial state to one fourth volume adiabatically. Its final pressure will be equal to
One mole of an ideal monoatomic gas is taken round the cyclic process ABCA as shown in fig. Calculate
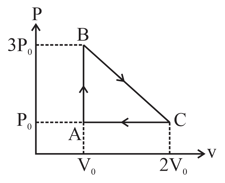
(a) The work done by the gas.
b) The heat rejected by the gas in the path and heat absorbed in the path .
(c) The net heat absorbed by the gas in the path .
A sound wave is travelling in a uniform pipe with gas of adiabatic exponent . If is the particle velocity at any point in medium and is the wave velocity, then relative change in pressure through this point is :-
An ideal gas is compressed such that its pressure and volume are related as = constant. During this process, the temperature of gas
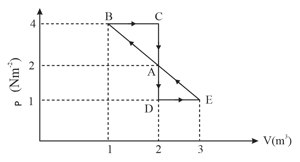
One mole of monoatomic gas is carried along process as shown in the diagram. Find the net work done by gas.
In which of the following process, the internal energy of gas remains constant?
A monoatomic gas initially at pressure and volume is compressed to of its volume adiabatically. Final pressure of the gas is equal to
Can two isothermal curves cut each other?
The final volume (in ) of one mole of an ideal gas initially at and pressure, if it absorbs of heat during a reversible isothermal expansion, is
The work done by gas is equal to heat supplied. An ideal gas has initial volume and pressure To triple its volume the minimum work done, will be
Following graph shows a single stage expansion process, then work done by the system is ?
A closed gas cylinder is divided into two parts by a piston held tight. The pressure and volume of gas in two parts respectively are and . If now the piston is left free and the system undergoes isothermal process, then the volume of the gas in two parts respectively are
The work involved in an isothermal expansion of moles of an ideal gas from an initial pressure of atm to final pressure of in number of steps such that in every step, the constant external pressure exactly less than the initial pressure of gas is maintained, is given as
Calculate the amount of work done when one mole of an ideal gas contained in a bulb of capacity at is allowed to enter in evacuated bulb of capacity and in another case it is allowed to expand from to against a pressure of .
