Critical Velocity and Reynolds Number
Critical Velocity and Reynolds Number: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Reynolds Number, Condition for Laminar Flow, Rate of Flow of a Fluid or Discharge 'Q', Inertial Force of Fluid in Motion, Critical Velocity, Significance of Reynolds Number & Unsteady Flow of Fluid etc.
Important Questions on Critical Velocity and Reynolds Number
The ratio of inertial force to viscous force represents:
Critical velocity is the velocity below which the flow of liquid is _____?
The critical velocity depends on the radius of the earth, mass of the earth and gravitational constant.
Define critical velocity?
. A beaker contains water up to a certain height as shown. If the water is allowed to get discharged through a small pipe (of a uniform diameter), what type of flow will it be in the pipe ?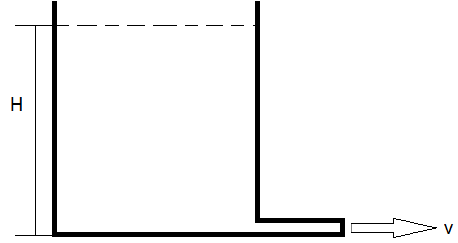
What is an unsteady flow?
In laminar flow, is reynold's number occurs below the critical value?
Motion of particles of the fluid is very orderly in _____.
Is laminar flow occurs when fluid flows in parallel layers?
Which of the following statements is true in the context of inertial force?
This force is the driving force in fluids.
What is the inertial force in fluids?
What would be the Reynolds number if the flow is streamlined?
What would be the Reynolds number if the flow is turbulent?
How does Reynolds number distinguish between laminar flow and turbulent flow?
Identify the turbulent flow from the following statements.
Define unsteady flow of liquid.
The ratio of inertial force to viscous force represents Reynolds number.
The onset of turbulence in a liquid is determined by: Reynold's number.
Which of the following options represent the ratio of inertial force to viscous force?
