Centre of Mass and Its Motion
Centre of Mass and Its Motion: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Centre of Mass, Centre of Mass of Two Particles, Centre of Mass of More than Two Particles, Centre of Mass of Symmetrical Bodies, Centre of Mass of Continuous Bodies, Velocity of Centre of Mass, etc.
Important Questions on Centre of Mass and Its Motion
Two spherical bodies of mass and and radii and respectively are released in free space with initial separation between their centres equal to . If they attract each other due to gravitational force only, then the distance covered by the smaller body just before collision is–
If the resultant of all the external forces acting on a body be zero, the centre of mass of the system
Two bodies of different masses and are moving with velocities and towards each other due to mutual gravitational attraction. Then the velocity of the centre of mass is
If the separation between carbon and oxygen in molecule is , then the distance of the center of mass from the carbon atom is
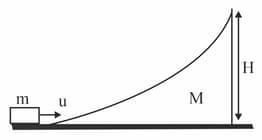
A block of mass is projected towards a wedge of mass with a velocity as shown in the figure below. All the surfaces are smooth. Find the expression for the maximum height attained by the block as it moves on the surface of the wedge.
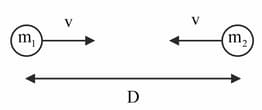
Two masses at a distance equal to are moving towards each other due to gravitational pull as shown in the figure below. Find the expression for the relative velocity of two masses when the distance between the two masses become .
The concept of reduced mass can be used in the problems where the force between the two masses is:
Two masses and are connected by a spring are kept on a frictionless table as shown in the figure below. The block of mass is imparted the velocity equal to towards right. Find the maximum compression in the spring.

What do you understand by reduced mass?
A uniform thin wooden plank of length and mass is kept on a table with its end slightly outside the edge of the table. When an impulse is given to the end , the plank moves up with centre of mass rising a distance from the surface of the table. Then,
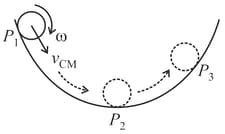
A small ring is rolling without slipping on the circumference of a large bowl as shown below in the figure. The ring is moving down at , comes down to the lower most point and is climbing up at . Let denote the velocity of the centre of mass of the ring. Choose the correct statement regarding the frictional force on the ring.
The distance between the carbon atom and the oxygen atom in a carbon monoxide molecule is . Given, mass of carbon atom is 12 a.m. and mass of oxygen atom is 16 a.m.u. Calculate the position of the centre of mass of the carbon monoxide molecule.
A tank with uniform cross-sectional area is filled with a liquid of density upto a height What is the potential energy stored in the system ? (where denotes the acceleration due to gravity)
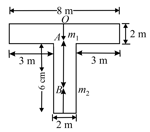
The distance of the centre of mass of the shaped plate from is,
Two particles of equal mass have velocities and . First particle has an acceleration while the acceleration of the other particle is zero. The centre of mass of the two particles moves in a path of
A man of mass stands at one end of a plank of length which lies at rest on a frictionless surface. The man walks to the other end of the plank. If the mass of plank is , the distance that the Man moves relative to the ground is:
A circular hole of radius is cut off from a disc of radius . The centre of the hole is from the centre of the disc. Then the distance of the centre of mass of the remaining disc from the centre of the disc is
For a bangle, the centre of mass lie outside the body.
The center of mass of a system of particles does not depend upon force acting on particle.
Two particles A and B initially at rest, move towards each other, under mutual force of attraction. At an instance when the speed of A is and speed of B is , the centre of mass (CM) remains at rest. This statement is _____. Choose from (True/False).
