Friction
Friction: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Laws of Friction, Friction on Inclined Plane, Methods to Decrease Friction, Necessity of Friction, Friction, Static Friction, Angle of Friction, Kinetic Friction, Graph of Frictional Force, etc.
Important Questions on Friction
Consider a car moving along a straight horizontal road with speed of . If the coefficient of static friction between the tyres and the road is , the shortest distance in which the car can be stopped is (taking )
A heavy uniform chain lies on a horizontal table-top. If the coefficient of friction between the chain and the table surface is , then the maximum fraction of the length of the chain that can hang over one edge of the table is
A conveyor belt is moving at a constant speed of . A box is gently dropped on it. The coefficient of friction between them is The distance that the box will move relative to belt before coming to rest on it taking , is
A block B is pushed momentarily along a horizontal surface with an initial velocity v. If is the coefficient of sliding friction between B and the surface, block B will come to rest after a time
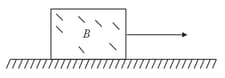
A person slides freely down a frictionless inclined plane while his bag falls vertically from the same height. The final speeds of the man and the bag should be such that :
Starting from rest, a body slides down a inclined plane in twice the time it takes to slide down the same distance in the absence of friction. The coefficient of friction between the body and the inclined plane is
A block of mass is held against a wall by applying a horizontal force of on the block. If the coefficient of friction between the block and the wall is the magnitude of the frictional force acting on the block is (take )
A block of mass rests on a rough inclined plane making an angle of with the horizontal. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the plane is The frictional force on the block is
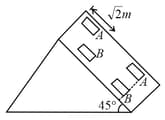
Two block and of equal masses are placed on a rough inclined plane as shown in figure. When (and where) will the two blocks come on the same line on the inclined plane if they are released simultaneously? Initially the block is behind the block . Co-efficient of kinetic friction for the blocks and are and respectively
In the figure masses and are and respectively. The coefficient of friction between and ground is zero. The coefficient of friction between and and that between and ground is The pulleys and the strings are massless. The string is perfectly horizontal between and and also between and The string is perfectly vertical between and An external horizontal force is applied to the mass Take
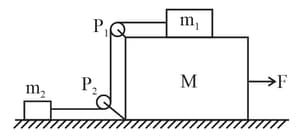
(a) Draw a free-body diagram for mass clearly showing all the forces.
(b) Let the magnitude of the force of friction between and be and that between and ground be For a particular it is found that Find and Write equations of motion of all the masses. Find tension in the string and acceleration of the masses.
Block of mass and block of mass are placed on a fixed triangular wedge by means of a massless inextensible string and a frictionless pulley as shown in figure. The wedge is inclined at to the horizontal on both sides. The coefficient of friction between block and the wedge is and that between block and the wedge is . If the system of and is released from rest, find the acceleration of .
Masses are connected by strings of negligible mass which pass over massless and frictionless pulleys as shown in the figure. The masses move such that the portion of the string between is parallel to the inclined plane and portion of the string between is horizontal. The masses are each and coefficient of kinetic friction between the masses and the surfaces is 0.25. The inclined plane makes an angle of with the horizontal. If the mass moves downwards with a uniform velocity, find the tension in the horizontal portion of the string.
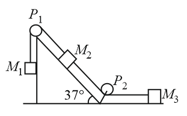
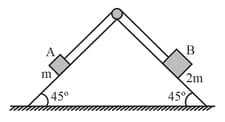
Two blocks connected by a massless string slide down an inclined plane having an angle of inclination of The masses of the two blocks are and respectively and the coefficients of friction of and with the inclined plane are 0.75 and 0.25 respectively. Assuming the string to the taut, find the tension in the string.
Two blocks connected by a massless string slide down an inclined plane having an angle of inclination of The masses of the two blocks are and respectively and the coefficients of friction of and with the inclined plane are and respectively. Assuming the string to be taut, find the common acceleration of two masses.
In the diagram shown, the blocks weight, respectively. The coefficient of sliding friction between any two surface is . A is held at rest by a massless rigid rod fixed to the wall while and are connected by a light flexible cord passing around a frictionless pulley. Find the force necessary to drag along the horizontal surface to the left at constant speed. Assume that the arrangement shown in the diagram, , is maintained all through.
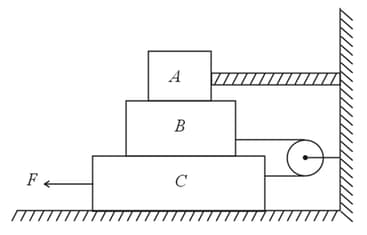
An insect crawls up a hemispherical surface very slowly (see the figure). The coefficient of friction between the insect and the surface is . If the line joining the center of the hemispherical surface to the insect makes an angle with the vertical, the maximum possible value of is given by,
a marble block of mass lying on the ice when given a velocity of is stopped by frictional force in . Then the coefficient of friction is
(take )
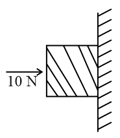
A horizontal force of is necessary to just hold a block stationary against a wall. The coefficient of friction between the block and the wall is . The weight of the block is –
The upper half of an inclined plane with inclination is perfectly smooth while the lower half is rough. A body starting from rest at the top will again come to rest at the bottom if the coefficient of friction for the lower half is
A block rests on a rough inclined plane making an angle of with the horizontal. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the plane is . If the frictional force on the block is , the mass of the block (in ) is (take: ),
