Impulse
Impulse: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Linear Impulse, Linear Impulse of Constant Force, Linear Impulse of Time Varying Force, Linear Impulse from F-T Diagrams & Impulse-Momentum Theorem etc.
Important Questions on Impulse
What are the conditions for calling a force as an impulsive force ?
Which law can be used to explain the following phenomena: A karate player breaks a pile of tiles or bricks with a single blow.
A cricket ball of mass moving with a velocity of is brought to rest by a player by moving his hands back by find impulse and time in which ball come to rest and force exerted by player
The impulse applied to a body is equal to the change in the __________ of that body.
Two billiard ball each of mass moving in opposite directions with speed collide and rebounds with the same speed. The magnitude of impulse imparted to each ball due to other is
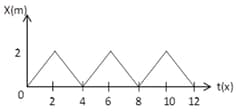
Figure shows the position–time graph of one dimensional motion of a body of mass . What is the time interval between two consecutive impulses received by the body?
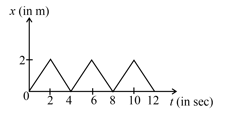
The figure shows the position-time graph of one-dimensional motion of a body of mass The interval between two consecutive impulses received by the body would be
A body of mass 10 kg is acted upon by a given equation Newton. The initial velocity of the body is 10 m/s. The velocity of the body after 5 sec is
At time t second, a particle of mass 3 kg has position vector metre where . The impulse of the force during the time interval is
A body of mass 5 kg is acted on by a net force F which varies with time t as shown in graph, then the net momentum in SI units gained by the body at the end of 10 seconds is
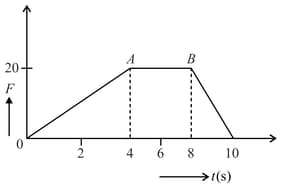
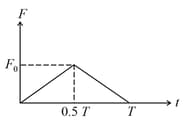
A body of has an initial speed . A force acts on it for in the direction of motion. The force-time graph is shown in figure. The final speed of the body after is
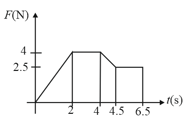
A ball of mass moving with a velocity rebounds from a wall. The collision is assumed to be elastic and the force of interaction between the ball and wall varies as shown in the figure. Then the value of is -
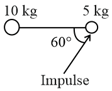
Two point masses connected by an ideal string are placed on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the diagram. A sharp impulse of is given to the mass. The velocity of the mass will be -
A sping balance is adjusted at zero. Elastic collisions are brought about by dropping particles of one gram each on the pan of the balance. They recoil upwards without change in their speed. If the height of fall of particles is and the rate of particle dropping is per second, then the reading of the balance is (take )
A disc of mass is kept floating horizontally in the air by firing bullets, each of mass , with the same velocity at the same rate of bullets per second. The bullets rebound with the same speed in positive direction. The velocity of each bullet at the time of impact is
A player kicks a football of mass and the football begins to move with a velocity of . If the contact between the leg and the football lasts for Then the force on the ball should be
A force-time graph for a linear motion of a body is shown in the figure. The change in linear momentum between and is
A hockey player receives a corner shot at a speed of at an angle of with the -axis and then shoots the ball of mass 100 g along the negative -axis with a speed of . If it remains in contact with the hockey stick for 0.01 s, the force imparted to the ball in the -direction is