Wedge-Block System
Wedge-Block System: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Motion on Wedges, Motion of Blocks on Wedge Moving with Constant Velocity, and Motion of Blocks on Wedge Moving with Constant Acceleration.
Important Questions on Wedge-Block System
A weight of is help on a smooth plane, inclined at to the horizontal by a force acting above the plane as shown by the figure. The reaction of the plane on the weight will be:
The co-efficient of friction and the angle of friction are related as
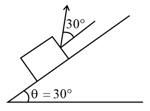
A body is resting on a plane inclined at angle , to horizontal. What force would be required to slide it down, if the co-efficient of friction between body and plane is ?
A box weight is placed on the ground. The co-efficient of friction between the box and th ground is . When the box is pulled by a horizontal force, the frinctional force developed between the box and ground at imepending motion is
A block of mass slides down from rest along a frictionless inclined plane that makes an angle of with horizontal. What will be the speed of the block after it covers a distance of along the plane?
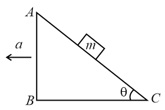
A body of mass is resting on a wedge having inclination as shown in figure. What is the acceleration of the wedge such that the mass just falls freely?
The value of for which the system is in equilibrium
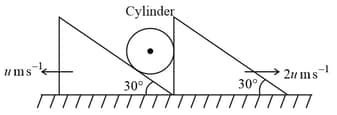
In the system shown in figure assume that cylinder remains in contact with the two wedges. The velocity of cylinder is
A system is accelerated upward with an acceleration . The apparent weight of a body of mass in the system is -
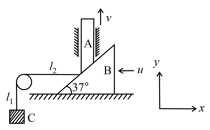
In the given figure, if the velocity of the block at a particular instant is , then the velocity of the rod (A) at that instant will be : (string is attached to wedge)
A body of mass is suspended by a spring balance on an inclined plane as shown in the figure. Measure the force applied on spring balance,
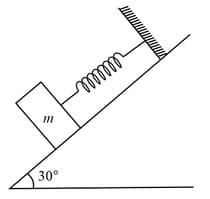
An ice tube is kept on an inclined plane of angle . The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and inclined plane is . What is the acceleration of the block?
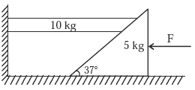
Block of mass and block of mass are placed on a fixed triangular wedge by means of a massless, inextensible string and a frictionless pulley as shown in figure. The wedge is inclined at to the horizontal on both the sides. The coefficient of friction between the block and the wedge is 2/3 and that between the block and the wedge is 1/3 and both the blocks and are released from rest, the acceleration of will be
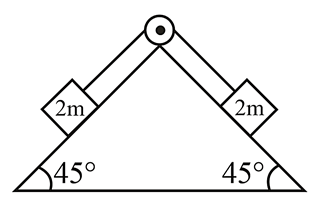
Two blocks of equal masses are released from the top of a smooth fixed wedge as shown in the figure. The acceleration of the centre of mass of the two blocks is
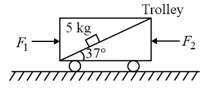
There is a trolley in which there is a fixed inclined surface on which a smooth block of mass is placed. Two horizontal forces of magnitude and are applied on the trolley as shown to keep the trolley at rest. The value of is : (Assume there is no friction between the trolley and horizontal ground and )
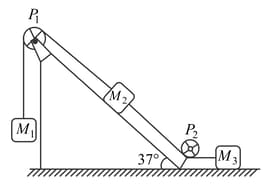
Masses, , and are connected by strings of negligible mass which pass over massless and frictionless pulleys and as shown in the figure. The masses move such that the portion of the string between and is parallel to the inclined plane and the portion of the string between and is horizontal. The masses and are each and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the masses and the surfaces is . The inclined plane makes an angle of with the horizontal and the mass moves downwards with a uniform velocity. Find the tension(in ) in the horizontal portion of the string.
(Take , )
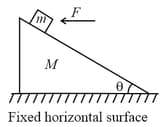
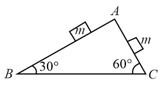
A block of mass lies on the wedge of mass , which lies on the fixed horizontal surface. The wedge is free to move on the horizontal surface. A horizontal force of magnitude is applied on the block as shown, neglecting friction at all surfaces, the value of force such that block has no relative motion with respect to the wedge will be (Where is the acceleration due to gravity)