Non-uniform Circular Motion
Non-uniform Circular Motion: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Angular Acceleration, Tangential Acceleration, Relation between Angular Acceleration and Tangential Acceleration and, Circular Motion with Increasing Speed
Important Questions on Non-uniform Circular Motion
The angular speed of a car increases from to in . What is the angular acceleration of the car?
An object is moving around a circular path of radius with speed of . The value of tangential acceleration in Uniform circular motion is
Which one is the correct relation between angular acceleration and tangential acceleration when a particle is moving along a circular path of radius .
A particle is moving along a circular path of radius with a tangential acceleration of . Calculate its angular acceleration.
Which one is the correct relation between angular acceleration and tangential acceleration when a particle is moving along a circular path of radius .
A solid body rotates with deceleration about a stationary axis with an angular deceleration , where is its angular velocity.The mean angular velocity of the body averaged over the whole time of rotation is if at the initial moment of time its angular velocity was equal to . Find .
For next two question please follow the same
In the diagram a block of mass m is connected to a spool of mass 3m, inner radius R and outer radius 2R as shown. The pulley is light and surface is sufficiently rough such that no sliding takes place. Let, the moment of inertia of spool is mR2 about the axis passing through centre of mass and perpendicular to the plane of rotation.
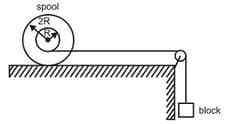
The system is released from rest, answer the following
The angular acceleration of spool is
The length of hour hand of a wrist watch is . Find magnitude of tangential acceleration.
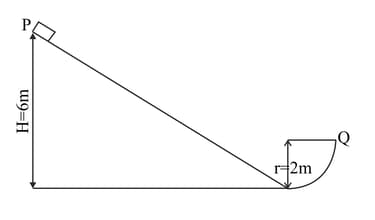
A block of mass is released from on a frictionless track which ends in quarter circular track of radius at the bottom. What is the magnitude of radial acceleration and total acceleration of the block when it arrives at.
A particle is moving in a circle with constant tangential acceleration. Which one of the following is constant?
A rotating flywheel about a fixed axis slows down from to in . What is angular retardation of flywheel (in SI unit)
A ball tied to the end of the string swings in a vertical circle under the influence of gravity.
When a particle is moving in a verticle circle, which of the following statement is true-
The figure shows a rod of mass m and length L attached on one end to a massless string of length l the other end of which is fixed to the ceiling. At this instant the string and rod make an angle θ with the vertical and the velocity of the lowest point of the rod is given to be ‘v’. The rod and string form a straight line at all times.
Find the angular acceleration of the rod at this instant?
The kinetic energy of a particle moving along a circle of radius R depends on the distance covered. It is given as , where is a constant. The force acting on the particle is
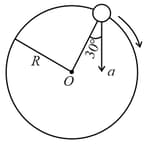
In the given figure, represents the total acceleration of a particle moving in the clockwise direction in a circle of radius m at a given instant of time. The speed of the particle is
For a hollow cylinder (of mass m and radius r) rolling without slipping on a horizontal surface, acceleration of the bottom-most point is equal to a (constant). Kinetic energy of the cylinder is
A Particle is moving in a circle of radius R in such a way that at any instant the normal and tangential component of the acceleration are equal. If its speed at is , the time taken to complete the first revolution is
A body is moving with a constant speed in a circle of radius . Its angular acceleration is
What happens to the centripetal acceleration of a revolving body if you double the orbital speed and halved the angular velocity ?
