Torque
Torque: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Torque, Angular Momentum, Conservation of Angular Momentum, Torque and Angular Momentum, Angular Momentum of Particle about a Fixed Axis, Torque of a Force about an Axis and, Torque of a Force about a Fixed Point
Important Questions on Torque
A planet of mass is in an elliptical orbit about the sun with an orbital period . If be the area of orbit, then its angular momentum would be
On the rotating disc of mass, another disc of same dimension but of massis placed gently with same axis. New angular velocity of system.
A particle of mass is moving along the line ( and are in meter) with speed . The magnitude of angular momentum of the particle about origin is
A bar of mass and length is lying on a horizontal frictionless surface. One end of the bar is pivoted at a point about which it is free to rotate. A small mass is moving on the same horizontal surface with speed on a path perpendicular to the bar. It hits the bar at a distance from the pivoted end and returns back on the same path with speed . After this elastic collision, the bar rotates with an angular velocity . Which of the following statement is correct?
A wheel of mass and radius of gyration comes to rest from a speed of insecond. Assuming that the retardation is uniform, the value of the retarding torque is :
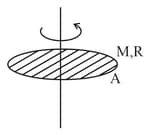
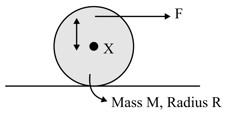
A force is applied on a disk at some distance from the centre. What should be the value of such that the disk can pure roll even on smooth surface?
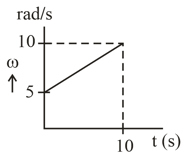
Angular speed versus time for a rod that rotates around one end is shown. If moment of inertia of rod about its one end is , then torque on the rod at is
A rod of mass and length is hinged at end . The rod is kept horizontal by a massless string tied to pointas shown in figure. When string is cut, the initial angular acceleration of the rod is (in ):-
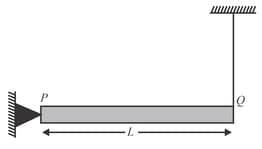
A sphere is released on a smooth inclined plane from the top. When it moves down its angular momentum is:
A uniform rod weighs and with a load attached to one end, it balances on a knife edge at from that end. The length of rod is
The angular momentum of a particle with respect to the origin will not be zero, if
Two persons stand at the edges of a rotating circular platform at diametrically opposite points. If they start moving towards each other at uniform velocity, then its
Horizontal rod of length given below is in equilibrium. If the potential energies of objects and are equal, find the tension (in N) in string . (Rod is homogeneous and weight of it is .
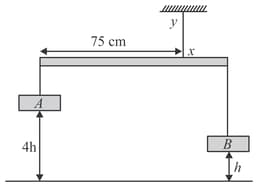
zero potential energy level
A uniform solid cylinder of mass and radius rotates about a fixed vertical frictionless axle with an angular speed of . A particle of mass now sticks on cylinder at a distance of from the axle. Magnitude of change in angular velocity (in ) of the cylinder is
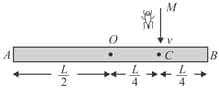
A homogeneous rod of length and mass is pivoted at the centre in such a way that it can rotate freely in the vertical plane. The rod is initially in the horizontal position. An insect of the same mass falls vertically with speed on the point mid-way between and . Determine the angular velocity in terms of and .
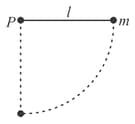
A bob of mass '' is suspended from point using a string of length ''. It is then pulled to a side till the string is horizontal and released as shown in figure. When the mass passes through the point where the string is vertical, magnitude of its angular momentum about point is
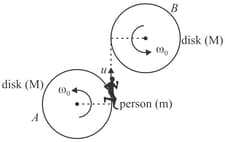
Two identical discs each of mass and radius are rotating in opposite sense with equal angular speed about vertical axes passing through their centres, (as shown in figure). A person of mass sitting on circumference of disc jumps with a tangential relative velocity (after jumping) w.r.t one rotating disc and lands on other disc also tangential. Now the second disc comes to a stop. Find the relative velocity .
The position vector and velocity vector of a particle of mass is given by and . Find when angular momentum is .
If force acts on a particle having position vector then, the torque about the origin will be:
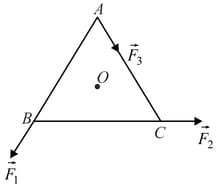
is an equilateral triangle with as its centre and . represent three forces acting along the sides and respectively. If the total torque about is zero then the magnitude of is