Radioactivity
Radioactivity: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Parent Nuclei, Daughter Nuclei, Change in Atomic Number after Alpha Decay, Change in Mass Number after Alpha Decay, Change in Atomic Number after Beta Decay, Gamma Ray Emission, Radioactive Decay Law, etc.
Important Questions on Radioactivity
Two nuclei have mass numbers in the ratio . The ratio of their nuclear radii would be:
The plot of the activity of a radioactive species versus time would be:
How long will a radioactive isotope, whose half life is years, take for its activity to reduce to of its initial value?
How long will a radioactive isotope, whose half-life is years, take for its activity to reduce to of its initial value?
Two nuclei have mass numbers in the ratio . The ratio of their nuclear radii is:
In decay, the terms half-life period and decay constant is used. The relationship between the two is
A radioactive sample contains of pure which has half-life period of . Calculate the number of atoms present initially and the activity when of the sample will be left.
In the Uranium radioactive series, the initial nucleus is and the final nucleus is . When the Uranium nucleus decays to lead, the number of particles emitted is _______________ and the number of particles emitted is _______________.
The half life of a radioactive substance isminutes. In how much time, the activity of substance drops to of its initial value?
The half-life of a radioactive nucleus is years. The fraction of the original sample that would decay in years is :
Two radioactive elements and initially have same number of atoms. The half life of is same as the average life of . If and are decay constants of and respectively, then choose the correct relation from the given options.
The decay constant for a radioactive nuclide is . Atomic weight of the substance is , . The activity of of the substance is ________ .
A radio active material is reduced to of its original amount in days. If of the material is left after days the initial amount of the material is
The half life of a radioactive substance is . The time taken, for disintegrating part of its original mass will be:
has half life of years. Find the amount of left after years.
If half life of a radio-active nuclide is equal to average life of another radio-active nuclide . Find the ratio of decay constant of to that of .
If half life for a radio active decay reaction is . Find the time after which of initial mass decays.
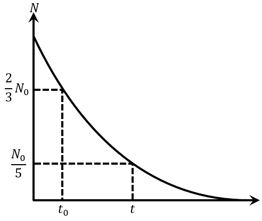
The graph shows the variation of the number of radioactive atoms left undecayed with time. The time corresponding to is:
Assuming of trace radioactive elementwith a half life of years is absorbed by a growing tree. The amount of remaining in the tree after years is.
[Given:;]
A radioactive element emits two -particles, one electron and two positrons. The product nucleus is represented by . The value of is ______.