Refraction at Spherical Surfaces and by Lenses
Refraction at Spherical Surfaces and by Lenses: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Lens, Concave Lens, Convex Lens, Lens Maker's Formula, Power of Lens, Paraxial Rays, Optical Centre, Focal Length of Lens, Lens Equation, Thin Lens, Principal Axis of Lens and, Refraction from Spherical Surface
Important Questions on Refraction at Spherical Surfaces and by Lenses
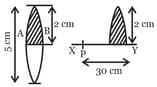
A converging lens of focal length 20 cm and diameter 5 cm is cut along the line AB. The part of the lens shown shaded in the diagram is now used to form an image of a point P placed 30 cm away from it on the line XY. Which is perpendicular to the plane of the lens. The image of P will be formed.
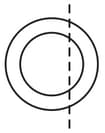
A spherical thick shell made of transparent material is cut along its chord as shown. The smaller part will
When the object is at distances u1 and u2 the images formed by the same lens are real and virtual respectively and of the same size. Then focal length of the lens is
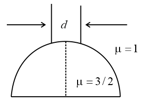
A beam of diameter 'd' is incident on a glass hemisphere as shown. If the radius of curvature of the hemisphere is very large in comparison to d, then the diameter of the beam at the base of the hemisphere will be
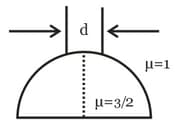
A beam of diameter is incident on a glass hemisphere as shown. If the radius of curvature of the hemisphere is very large in comparison to , then the diameter of the beam at the base of the hemisphere will be
A concave spherical surface of radius of curvature 10 cm separates two medium x & y 0f refractive index 4/3 & 3/2 respectively. If the object is placed along principal axis in medium X then
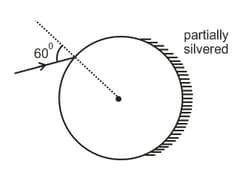
A ray is incident on a glass sphere as shown. The opposite surface of the sphere is partially silvered. If the net deviation of the ray transmitted at the partially silvered surface is 1/3rd of the net deviation suffered by the ray reflected at the partially silvered surface (after emerging out of the sphere). Find the refractive index of the sphere.
A thin convex lens forms a real image of a certain object 'p' times its size. The size of real image becomes 'q' times that of object when the lens is moved nearer to the object by a distance 'a' find focal length of the lens?
Two thin lenses of power +6D and –2D are in contact. The focal length of the combination would be:
A thin lens of refractive index has a focal length of in air. When the lens is placed in a medium of refractive index its focal length will become _________ .
An eye specialist prescribes spectacles having a combination of convex lens of focal length 40 cm in contact with a concave lens of focal length 25 cm. The power of this lens combination in diopters is
Two thin lenses are put close to each other. The focal length of the combination is:
A converging on a screen when the upper half of the lens of covered by opaque screen.
Explain the paraxial rays?
Define a method to measure the radii of curvature of lens.
A concave lens always produces a _____ (real and inverted/virtual and erect/real and erect/virtual and inverted) image of the real object.
Optical centre of a lens is important because it enables us to see the object more clearly without _____.
Is optical centre and centre of curvature same?
Explain optical centre of a lens with the help of proper diagrams?
What do you mean by focal plane of a lens ?
