Lens
Lens: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Lens, Thin Lens, Thick Lens, Lens Surface Nomenclature, Two Foci of Lens, Focal Length of Lens, Optical Centre, Centers of Curvature of a Lens, Principal Axis of Lens, Paraxial Rays, and Lens Equation.
Important Questions on Lens
A convex lens forms an object on a screen. The height of the image is 9 cm. The lens is now displaced until an image is again obtained on the screen. The height of this image is 4 cm. The distance between the object and the screen is 90 cm.
Which of the following can form diminished, virtual and erect image of your face
A lens is placed in the coordinate system such that its optical center is at the origin and the principal axis is along the axis. The focal length of the lens is . A point object has been placed at the point (). Which of the following are correct about coordinates of the image?
A planoconvex lens, when silvered at its plane surface is equivalent to a concave mirror of focal length . When its curved surface is silvered and the plane surface not silvered, it is equivalent to a concave mirror of focal length , then the refractive index of the material of the lens is
the curvature radii of a concavo-convex glass lens are and . The convex surface of the lens is silvered. With the lens horizontal, the concave surface is filled with water. The focal length of the effective mirror is ( of glass = , of water = )
A point object is kept just beyond the first focus of a convex lens. If the lens starts moving towards the right with a constant velocity, the image will
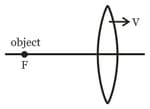
A screen is placed from an object. The image of an object on the screen is formed by a convex lens at two different locations separated by . The focal length of the lens is
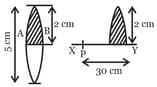
A converging lens of focal length 20 cm and diameter 5 cm is cut along the line AB. The part of the lens shown shaded in the diagram is now used to form an image of a point P placed 30 cm away from it on the line XY. Which is perpendicular to the plane of the lens. The image of P will be formed.
An object is placed in front of a thin convex lens of focal length 30 cm and a plane mirror is placed 15 cm behind the lens. If the final image of the object coincides with the object, the distance of the object from the lens is
A thin lens of focal length and its aperture has a diameter . It forms an image of intensity . Now the central part of the aperture upto diameter is blocked by an opaque paper. The focal length and image intensity would change to
A object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm. On the other side of the lens, a convex mirror is placed at its focus such that the image by the combination coincides with the object itself. The focal length of the convex mirror is
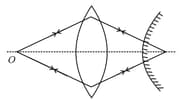
Parallel beam of light is incident on a system of two convex lenses of focal lengths and . What should be the distance between the two lenses so that rays after refraction from both the lenses pass undeviated
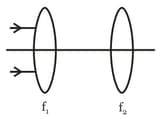
When the object is at distances u1 and u2 the images formed by the same lens are real and virtual respectively and of the same size. Then focal length of the lens is
A plano-convex lens has maximum thickness of 1 mm. If diameter of its aperture is 4 cm, then, the radius of curvature of curved surface and its focal length in air are respectively
A point source of light is kept at a distance of from a converging lens, on its optical axis. The focal length of the lens is and its diameter is . A screen is placed on the other side of the lens, perpendicular to the axis of the lens, at a distance . from it. Then find the area of the illuminated part of the screen?
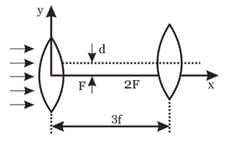
In the figure shown, the focal length of the two thin convex lenses is the same = f . They are separated by a horizontal distance 3 f and their optical axes are displaced by a vertical separation 'd' (d<<f), as shown. Taking the origin of coordinates O at the centre of the first lens, find the x and y coordinates of the point where a parallel beam of rays coming from the left finally get focussed?
A thin convex lens forms a real image of a certain object 'p' times its size. The size of real image becomes 'q' times that of object when the lens is moved nearer to the object by a distance 'a' find focal length of the lens?
An objective is kept at a distance of from a thin lens and the image formed is real. If the object is kept at a distance of from the same lens the image formed is virtual. If the size of the images formed are equal, then find the focal length of the lens?
A double convex lens has focal length of in air. The radius of one of the surfaces is double of the other. Find the radii of curvature, if the refractive index of the material of the lens is .
Two thin lenses of power +6D and –2D are in contact. The focal length of the combination would be:
