Refraction of Light at Plane Surface
Refraction of Light at Plane Surface: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Refraction from Plane Surface, Deviation in Refraction, Shift of Image Due to Refraction, Apparent Depth and Apparent Height, Apparent Depth for One Liquid, Refraction from Single Slab, etc.
Important Questions on Refraction of Light at Plane Surface
The phenomenon that takes place due to the bending of light when it travels from medium to another is known as
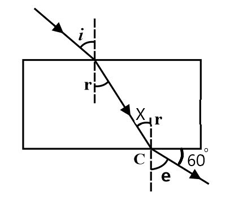
The angle of deviation produced by the glass slab is
For a certain parallel-sided glass block, the value of is . A ray of light passes through the block and emerges at an angle of to the surface of the block. What is the value of the angle marked X?
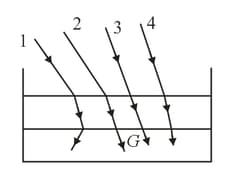
The optical density of turpentine is higher than that of water while its mass density is lower. Figure shows a laycr of turpcntine floating over water in a container. For which one of the four rays incident on turpentine in figure, the path. shown is correct
Cotyledons are also called-
A travelling microscope is used during the experiment
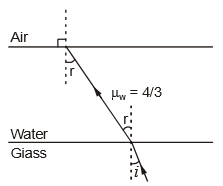
A ray of light is incident at the glass-water interface at an angle it emerges finally parallel to the surface of water, then the value of would be
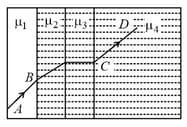
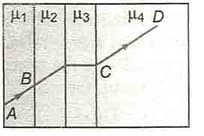
A ray of light passes through four transparent media with refractive indices and as shown in figure, the surfaces of all media are parallel. If the emergent ray CD is parallel. If the emergent ray CD is parallel to the incident ray AB, we must have
Light is incident at an angle i on a glass slab. The reflected ray is completely polarised. The angle of refraction is
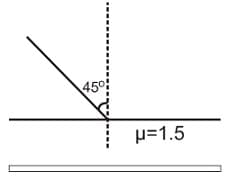
One side of a glass slab is silvered as shown. A ray of light is incident on the other side at angle of incidence . Refractive index of glass is given as 1.5. The deviation of the ray of light from its initial path when it comes out of the slab is:
Assertion: A parallel beam of light travelling in the air can be displaced laterally by a parallel transparent slab by a distance more than the thickness of the plate.
Reason: The lateral displacement of light travelling in the air increases with rise in the value of refractive index of the slab.
Assertion: If a plane glass slab is placed on the letters of different colours all the letters appear to be raised up to the same height.
Reason: Different colours have different wavelengths.
A vessel of depth is half filled with a liquid of refractive index and the upper half with a liquid of refractive index . The apparent depth of the vessel seen perpendicularly is
A ray of light passes through four transparent medium with refractive indices and as shown in the figure. The surfaces of all media are parallel. If the emergent ray is parallel to the incident ray AB. We must have
A piece of plane glass is placed on a word with letters of different colours. The letters which appear minimum raised are
A glass slab of thickness 6 m is placed over a paper. What is the shift in the shift in the letters?
A fish at a depth of in water is viewed by an observer on the bank of a lake. To what height the image of the fish is raised?
(Refractive index of like water)
The graph between angle of deviation (δ) and angle of incidence (i) for a triangular prism is represented by
A microscope is focussed on a mark a piece of paper and then a slab of glass of thickness 3 cm and refractive index 1.5 is placed over the mark. How should the microscope be moved to get the mark in focus again ?
Light propagates 2 cm distance in glass of refractive index 1.5 in time t0. In the same time t0, light propagates a distance of 2.25 cm in a medium. The refractive index of the medium is
