Coherent and Incoherent Addition of Waves
Coherent and Incoherent Addition of Waves: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Coherence of Light Waves, Principle of Superposition, Standard Interference Patterns & Monochromatic Light Waves etc.
Important Questions on Coherent and Incoherent Addition of Waves
Which is following statement is correct?
The minimum path difference between two light waves is equal to zero.
Path difference of corresponds to a phase difference of .
Two sources of monochromatic light are said to be coherent, if light waves produced by them have the same
Maxima and minima are produced when the path difference between waves is a whole number of wavelength or odd number of half wavelength.
What is the path difference for the first order maxima of wavelengths .
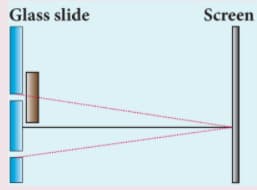
One of the Young's double slits is covered with a glass plate as shown in the figure. The position of central maxima will:
Two coherent monochromatic light beams of intensities and are superposed. The maximum and minimum possible intensities in the resulting beam are:
What is phase of a wave
Monochromatic light is that light in which :-
A point is situated at and from two coherent sources. Find the nature of illumination at the point if wavelength of light is
Using analytical method, obtain an expression for the path difference between two light waves.
Find the ratio of intensities at two points x and y on a screen in Young's double-slit experiment, where waves from and have path
difference of (i) and (ii)
State the conditions to get constructive and destructive interference of light.
What are coherent sources? How are they produced?
If the intensity ratio of two coherent sources used in Young's double slit experiment is 49: 1, then the ratio between the maximum and minimum intensities in the interference pattern is
In Young's double slit experiment, interference pattern is found to have an intensity ratio between bright and dark fringes as 9. Then amplitude ratio will be
Two waves and superimpose to produce a resultant wave. Amplitude of the resultant wave is
If ratio of intensities of two waves is 4 : 1, then ratio of amplitude of two waves is given by
If two waves of same frequency and same amplitude superimpose and produce a third wave of same amplitude, then waves differ in phase by
