Polarisation
Polarisation: Overview
This topic consists of various concepts like Polarisation of Light Waves,Terms in Polarisation,Linearly Polarised Light Waves, etc.
Important Questions on Polarisation
The angle at which the intensity of transmitted light becomes maximum when a polarising sheet is rotated between two crossed polaroids is
[ is the angle between transmission axes of first and middle polaroid]
Light, from a sodium lamp, is passed through two Polaroid sheets, and kept one after the other. Keeping fixed, is rotated so that its ‘pass – axis’ can be at different angles, with respect to the pass – axis of .
An experimentalist records the following data for the intensity of light coming out of as a function of the angle .
|
S. No. (Angle between the pass axis of the two polaroids) |
|||||
| (Intensity of light coming out of ) | 0 |
= Intensity of beam falling on
One of these observations is not in agreement with the expected theoretical variation of I. Identify this observation.
Two polaroids are set in crossed positions. A third polariser is placed between the two making an angle with the pass axis of the first polaroid. In what orientations(of third polaroid with respect to first polaroid) will the transmitted intensity be (i) minimum and (ii) maximum?
Unpolarised light of intensity passes through the combination of three polaroids such that the pass axis of the last polaroids is perpendicular to that of the pass axis of first polaroids. If intensity of emerging light is , then the angle between pass axis of first two polaroids is _________.
A light ray incident from a medium to another medium then the angle of polarization will be:
Two rays of light and are falling on a glass slab at the angles of incidence and . If the reflected ray of is partially polarized and that of is completely polarized, then the refractive index of glass is
Find the polarization angle for a medium which has the critical angle of incidence equal to .
A light whose electric field vectors are completely removed by using a good polaroid, allowed to incident on the surface of the prism at Brewster's angle. Choose the most suitable option for the phenomenon related to the prism.
For which angle of incidence, the reflected light is completely polarized?
Two polarisers are placed parallel to each other in the path of a beam of unpolarized light of intensity . The intensity of emergent beam is . If the first polariser is rotated about the line shown.
In a YDSE arrangement the separation between screen and slits is , while the separation between the slits is and wavelength of light used is . Intensity due to each slit is . A point ' ' is located above the central maxima at a distance equal to the wavelength. If the slits are separating at a rate of , the rate at which intensity at is changing is , find
Why the intensity of unpolarized light is reduced by half when passing through a polariser?
A beam of laser light is incident on an analyzer which is rotated on a spectrometer stage. If the intensity of the transmitted light changes from maximum to minimum (not zero), the nature of the incident beam is
Unpolarized red light is incident on the surface of a lake at a grazing angle . An observer seeing the light reflected from the water surface through a polarizer notices that on rotating the polarizer, the intensity of light drops to zero at a certain orientation. The red light is replaced by unpolarized blue light. The observer sees the same effect with reflected blue light at a grazing angle . Then,
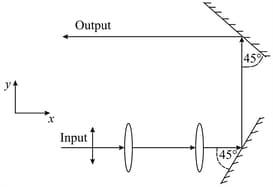
A parallel beam of light, linearly polarized along the y-axis, passes through a combination of convex lenses and mirrors as shown in the figure. The output beam
What happens when the angle of incidence is greater than polarising angle?
Unpolarized light having an intensity passes through a stack of polarizers, the pass axis of each of the polarizer makes an angle of with the axis of the preceding one. The intensity of light coming out of the last polarizer is
