Forced Oscillations and Resonance
Forced Oscillations and Resonance: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Forced Oscillations, Condition for Resonance, Behaviour of Forced Oscillation When Driving Frequency is Close to Natural Frequency & Free Oscillations etc.
Important Questions on Forced Oscillations and Resonance
The frequency of free oscillation called _____ frequency.
In a free oscillation,what happens to the amplitude,frequency and energy of the oscillating body?
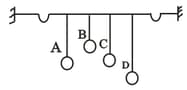
In the given arrangement which pair can represents the resonance.(All are simple pendulum).
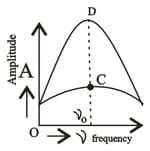
The variation of amplitude of forced oscillation vs driving frequency. Which part represents least damping.
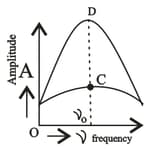
The variation of amplitude of forced oscillation vs driving frequency, which point represents the heavy damping.
A famous magic trick involves a performer singing a note towards the crystal glass shatters. Explain.
Natural frequency is also known as eigenfrequency.
For getting normal frequency in the oscillator we need to apply external force to oscillate the system.
What is a natural frequency?
A trolly of mass is connected to two identical springs, each of force constant . The trolly is displaced by and released. Calculate :
(A) the period of ensuing oscillations.
(B) The maximum speed of the trolley.
(C) total energy dissipated by the time trolley comes to rest due to damping force?
What are coupled oscillations?
Describe an illustration of free, forced and resonant oscillations.
A horizontal spring block system of mass execute SHM When the block is passing through its equilibrium position , an object of mass is put on it.and the two move together. Find the new amplitude and frequency of the vibration.
Derive the expression for the time period and the energy of a damped oscillator when the driving frequency is far from its natural frequency.
Derive a differential equation for a damped S.H.M.
What is the frequency with which forced periodic oscillations oscillate?
A vibrating system is analysed, and it is found that two successive oscillations have amplitudes of and respectively. The damping ratio of the system is:
A mass of is suspended from a spring of stiffness . The system is fitted with a damper with a damping ratio of . The mass is pulled down and then released. Calculate the damped frequency.
A mechanical system is oscillating at resonance with a constant amplitude. Which one of the following statements is not correct?
