First Law of Thermodynamics and Its Applications (Only for Ideal Gases)
First Law of Thermodynamics and Its Applications (Only for Ideal Gases): Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, First Law of Thermodynamics, Sign Convention in Thermodynamics, Cyclic Process without Indicator Diagrams & Polytropic Process etc.
Important Questions on First Law of Thermodynamics and Its Applications (Only for Ideal Gases)
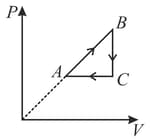
One mole of an ideal gas undergoes two different cyclic processes and , as shown in the diagrams below. In cycle , processes and are isobaric, isothermal, isobaric and isochoric, respectively. In cycle , processes and are isothermal, isochoric, isobaric and isochoric, respectively. The total work done during cycle is and that during cycle is . The ratio is _____.
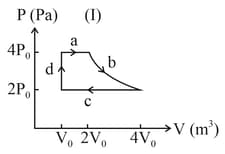
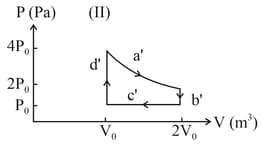
A closed container contains a homogeneous mixture of two moles of an ideal monatomic gas and one mole of an ideal diatomic gas . Here, is the ratio of the specific heats at constant pressure and constant volume of an ideal gas. The gas mixture does a work of Joule when heated at constant pressure. The change in its internal energy is _____ Joule.
One mole of an ideal gas expands adiabatically from an initial state to final state . Another mole of the same gas expands isothermally from a different initial state to the same final state . The ratio of the specific heats at constant pressure and constant volume of this ideal gas is . What is the ratio ?
What is for the process described by figure. Heat supplied during the process is .
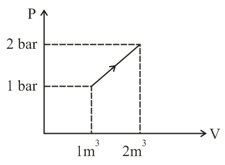
How the first law of thermodynamics can be justified? Give an example in support of your answer.
In the given diagram, a monoatomic gas is first compressed adiabatically from state state . Then it expands isothermally from state to state . [Given : ].
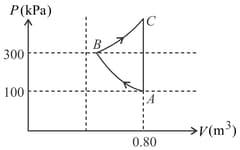
Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
An ideal gas of density enters a chimney of height at the rate of from its lower end, and escapes through the upper end as shown in the figure. The cross-sectional area of the lower end is and the upper end is . The pressure and the temperature of the gas at the lower end are and , respectively, while its temperature at the upper end is . The chimney is heat insulated so that the gas undergoes adiabatic expansion. Take and the ratio of specific heats of the gas . Ignore atmospheric pressure.
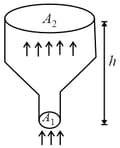
Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
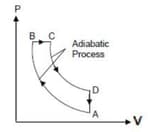
An idealized diesel engine operates in a cycle known as air standard diesel cycle as shown. Fuel is sprayed into the cylinder at the point of maximum compression . Combustion occurs during expansion .
moles of an ideal gas is taken through a cyclic process . Pressure - density diagram of which is shown in adjacent figure. If molar mass of gas is , what will be the work done by gas in cycle.
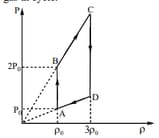
Figure shows a long fixed container which has two freely movable (without friction) pistons. The container and pistons are made up of a thermally conducting material, that allows very slow transfer of heat. First compartment of container is filled with moles of an ideal monoatomic gas at and the compartment is filled with 1 moles of ideal diatomic gas at . Initially pressure of gases in both the compartment is same and equal to atmospheric pressure. Temperature of atmosphere is . Finally gases achieve equilibrium. '' is the gas constant

A cylindrical container contains hydrogen in gaseous state under a light piston. The container and the piston both are very good insulators of heat. Initially the piston stays at a height above the bottom of the container in equilibrium. A ball of mass is dropped from a height above the piston collides elastically with the piston. When all motion ceases and equilibrium is reestablished, the piston again stays at the height
Neglect air resistance and take acceleration due to gravity as Mark the CORRECT statement(s)
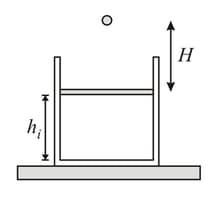
Two identical adiabatic vessels are filled with oxygen at pressure and The vessels are interconnected with each other by a non-conducting pipe. If and denote initial internal energies of oxygen in first and second vessels respectively and and denote final internal energies respectively, then
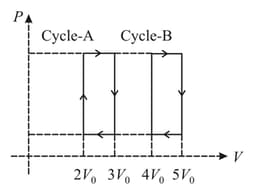
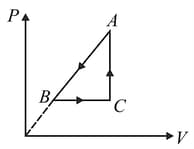
A heat engine used one mole of an ideal monatomic gas as a working substance. The engine can follow either cycle or cycle in the diagram. The ratio of the efficiencies of the cycles is If the value of is Find the value of
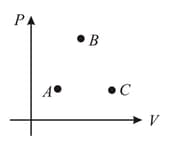
An ideal gas can expand from state to (via state through two different processes and In process and are straight lines in diagram. In process states
are on a circle in diagram. Heat supplied and work done by gas in process and are respectively and
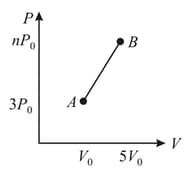
One mole of a monoatomic ideal gas follows a process as shown and The average molar heat capacity for the process is The value of on axis (see following figure) is
A cylindrical vessel is divided in two parts by a fixed partition which is perfectly heat conducting. The wall and piston are thermally insulated from surroundings. The left side contains moles of gas with at temperature of The right side contains moles of a mixture of gases with at same temperature of The piston compresses slowly the right side from volume of to Find the total change in internal energy of gases. (take unit and consider ideal gases only)
A container filled with air under pressure contains a soap bubble of radius The air pressure has been reduced to half isothermally and the new radius of the bubble becomes If the surface tension of the soap water solution is is found to be unit. Find
diagram of cyclic process is as shown in figure. Choose the correct statement(s)
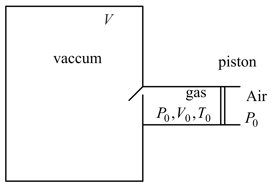
A large vacuum chamber of volume '' is connected to a narrow cylindrical pipe which is initially filled with an ideal gas at temperature $T_{0}$, pressure and volume . The gas is enclosed by a light insulating piston (which is free to move) and the air outside is constant pressure. Now the gas in the pipe slowly allowed to leak into the vacuum chamber through a small opening as shown. All the walls are insulated. The final pressure '' and temperature '' of the gas are given by
Consider a thermodynamic cycle in a diagram shown in the figure performe by one mole of a monoatomic gas. The temperature at is and volume at and are related as . Choose the correct option(s) form the following