Energy of a Particle Performing S.H.M
Energy of a Particle Performing S.H.M: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Kinetic Energy in Terms of Displacement in SHM,Potential Energy in Terms of Displacement in SHM,Total Energy with Displacement in SHM etc.
Important Questions on Energy of a Particle Performing S.H.M
One end of an ideal spring (spring constant) is attached to a rigid wall and other end to a block kept on a horizontal smooth surface. The spring is always horizontal. The block is released from rest when the spring is elongated by .
A body of mass falls freely from a height of , on a platform of mass which is mounted on a spring having spring constant. The body sticks to the platform and the spring's maximum compression is found to be. Given that , the value of will be close to
Total energy of a particle of mass performing linear SHM is . Find its maximum velocity.
The potential energy of a long spring when stretched by is . If the spring is stretched by , potential energy stored in it will be:
At a given point of time the value of displacement of a simple harmonic oscillator is given as If amplitude is and kinetic energy at that time is the value of force constant . The value of is _____.
A particle executes SHM of amplitude. The distance from the mean position when its kinetic energy becomes equal to its potential energy is:
A particle is executing simple harmonic motion (SHM). The ratio of potential energy and kinetic energy of the particle when its displacement is half of its amplitude will be
The variation of kinetic energy (KE) of a particle executing simple harmonic motion with the displacement () starting from mean position to extreme position () is given by
A particle is performing S.H.M whose distance from mean position varies as . Find the position of particle from mean position, where kinetic energy and potential energy is equal.
A particle is performing SHM having position and . If its kinetic energy at this position is , the value of force constant in is
Work done to elongate a spring by from natural length is. Which of the following is correct?
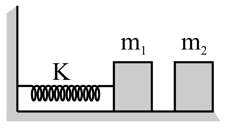
Masses and and a spring whose spring constant is are arranged according to the following figure. If the masses and are displaced towards left so that they compress the spring through a distance , the amplitude of oscillation of mass when the spring system is made free, will be-
When a body of mass m is suspended from a spiral spring of natural length, the spring gets stretched through a distance . The potential energy of the stretched spring is
A particle is undergoing SHM, when its kinetic energy is equal to potential energy, the velocity of particle is ( angular frequency, - amplitude and potential energy at mean position is zero)
A particle is executing SHM. At a point , kinetic energy of the particle is , where is the amplitude. At a point , kinetic energy of the particle will be:
A spring of force constantis cut in two parts at its one third length. When both the parts are stretched by same amount, the work done in the two parts, will be
(1) equal in both
(2) greater for the longer part
(3) greater for the shorter part
(4) data insufficient
A sphere of mass and radius rolls without sliding on a horizontal surface. It collides with a light spring of stiffness with a kinetic energy . If the surface under the spring is smooth and and , find the maximum compression of the spring.
Derive the expression for total energy in simple harmonic motion.
Initially mass is held such that spring is in relaxed condition. If mass is slowly released, maximum elongation in spring will be
The elastic potential energy stored in a spring, having a compression , is . The potential energy stored in spring, when it is given an extension of from its natural length, is
