Flowers : Structure and Types
Flowers : Structure and Types: Overview
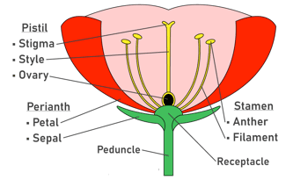
This topic covers concepts such as Thalamus of Flower, Calyx, Corolla, Androecium, Gynoecium, Flower, Unisexual Flowers, Bisexual Flowers, Filament of Stamen, Anther of Stamen, Ovary of Flower, Style of Pistil, Stigma of Pistil, Ovules, etc.
Important Questions on Flowers : Structure and Types
Give some examples of short night duration plants.
Write a short note on disc floret.
Ray florets of sunflower are _____ and _____.
Look at the given picture carefully and answer the question.

Choose the correct name of the picture from the given options.
Look at the picture carefully and write which part of the flower contains nodes and internodes.
Select the odd one out from the given options.
Fill in the blank with a suitable word given in the bracket.
_____ supply nutrients to flowers. (Petals/ Thalamus/ calyx)
Observe the picture of the flower given below and identify the part thalamus.
Filament is the tube-like structure that holds up the stigma.
Which of the following is the labelled part 'A' in the flower?
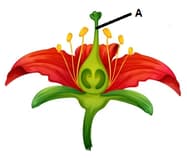
Which of the following is the labelled part 'A' of the flower in a given picture?
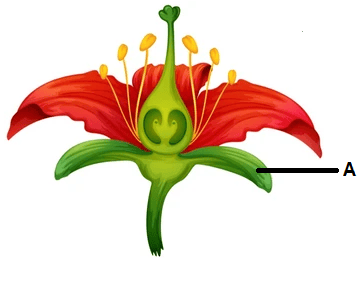
Write the function of style in a flower.
Define sepals in a flower.
What is corolla and its function?
An incomplete flower has sepals, petals, pistils and stamens.
Choose the incomplete flower.
A complete flower has only stamen.
Choose the correct answer from the box and fill in the blank:
| calyx | androecium | gynoecium |
The _____ is the whorl of the flower that contains pistil.
The pistil consists of filaments and anthers.
Which is the part of the pistil.
