Image Formation by Spherical Mirrors
Image Formation by Spherical Mirrors: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Images by Convex Mirror for Different Positions of an Object, Image Formation by Concave Mirror,Images by Concave Mirror for Different Positions of an Object and Image Formation by Spherical Mirrors Using Ray Diagram etc.
Important Questions on Image Formation by Spherical Mirrors
A thin road of length d/3 is placed along the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length = d such that its image, which is real and elongated, just touches the rod. Find the length of the image?
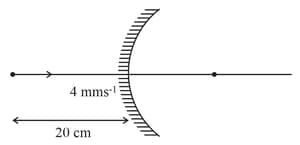
An object is moving with in front of a convex mirror () as shown in figure. Find speed of image if the mirror is stationary
The light that reaches the telescopes comes from very far away celestial objects. Draw a ray diagram to show what happens when light from a far away object falls on a convex mirror and a concave mirror.
A student determines the focal length of a device 'X' by focusing the image of a distant object on a screen placed from the device on the same side as the object. The device 'X' is
Name the mirror which can show the size of the object to be double of its original.
A candle is placed away from a convex mirror of focal length . Give the location of the image and the magnification.
What is the type of nature of image formed for an object placed an axis of concave mirror between pole and centre?
A student get a real image of an object of height of , when kept at from a spherical mirror of focal length . What is the type of mirror he/she used? What is the position, nature and size of the image formed?
A student get a virtual image of an object of height of , when kept at from a spherical mirror of focal length . What is the type of mirror he/she used? What is the position, nature and size of the image formed?
Image of an object situated at a distance of from a convex mirror is formed at a distance of from the mirror. Find the focal length of convex mirror.
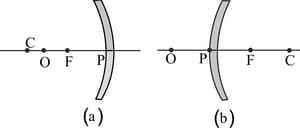
In the given figures, locate the image formed by using an appropriate ray diagram of a point object O shown in the figure using laws of reflection.
Using mirror formula prove that an object kept at forms its image at in front of a concave mirror.
Incident parallel rays make an angle of with the axis of a concave mirror of focal length at pole of the mirror. The perpendicular distance of image from the axis is nearly.
A concave mirror has a focal length of . A rod of length is placed along the principal axis of the mirror in such a way that the end closer to the mirror lies on its centre of curvature. The length of the image of the rod is
How the real image is inverted in the spherical mirror?
If image of '' is formed at '' itself find values of ''.
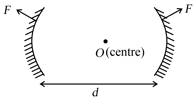
A cube of side is placed in front of a concave mirror focal length with its face at a distance of and face at a distance of from the mirror. Then,
An object of height is placed in front of a concave mirror and virtual image of height is obtained. If the object is placed at from the concave mirror, the focal length of mirror is
Draw the ray diagram when of image formed the object is kept beyond of the concave mirror. With the help of the diagram mention the position and nature of the image formed. ( : Centre of curvature of mirror).
Find the magnification produced by a convex mirror of focal length , if the object is kept at a distance of from the mirror.
