Refraction Through Lens
Refraction Through Lens: Overview
In this topic, we will understand the concepts related to light and its reflection. It explains the effect of reflection of light on viewing of an object. We will also study the laws of reflection, image formation by mirrors and lateral inversion.
Important Questions on Refraction Through Lens
Which of the following can form diminished, virtual and erect image of your face
Two plano convex lenses each of focal length and refractive index are placed as shown. In the space left, water (R.I) is filled. The whole arrangement is in the air. The optical power of the system is (in diopters)
The height of the image formed by a converging lens on a screen is 8 cm. For the same position of the object and screen again of size 12.5 cm is formed on the screen by shifting the lens. The height of the object
If an object is placed at the focus of a convex lens, its image is
How do you say that the focal length of a concave lens is always negative?
An object is placed at a distance from a convex lens of focal length . Select the correct image distance and nature of the image.
The convex lens always gives small virtual image.
An object is put at a distance from the optical centre of a convex lens. If its real image is formed at a distance from the lens then its focal length is about -
A ray of light is incident on a lens parallel to its principal axis. After refraction, the ray passes through or appear to come from:
The focal length of a convex lens is . The images formed is double the length of the object. The distance of the object from the lens is
If be the focal length of a convex lens, then the nature of image of an object placed at a distance will be :
The central point of a lens is known as:
A thin lens produces a sharp image of an object on the wall. The distance between the object and the wall is times the distance of the wall from the nearest focal point. The object magnification is
Two rays coming parallel to principal axis falls on plano concave lens which is separating air from other two medium as shown in the
diagram. The incident rays enter the medium K, L and through lens M. Based on the information given in the diagram arrange the values of refractive indices of medium and choose the appropriate option.
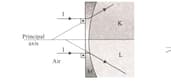
Figure given shown the ray diagram of incident ray I, falling on concave lens, represents the focal length of the lenses. Then based on the information in the diagram, choose the appropriate answer option.
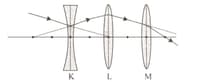
The rays coming to the system formed by divergent X and convergent Y lenses whose principal axes are coincident and focal lengths are as shown in the figure.
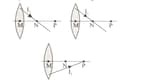
Accordingly, which of the rays have been given the correct path after the second time in the lens?
(Distances between points are equal and about.)
Half of the X and Y lenses with refractive indices are in K environment with refractive index and half in L medium with refractive index . As a result of the beam refractions. it leaves the lens system as the beam.
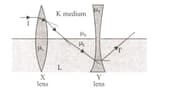
So what is the relationship between ?
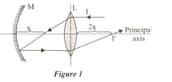
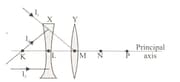
The I-ray, which is sent parallel to the principal axis, to the optical system formed by the L thin- edged lens with coincident principal axes and the M concave mirror, leaves the system as I' beam as a result of reflection and refraction. According to this,
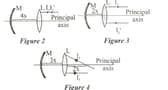
Accordingly, which of the rays can the I beam leave the system in the optical devices in Figure 2. Figure 3 and Figure 4 formed by the M mirror and L lens?
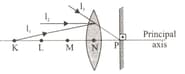
rays are sent to the optical mechanism formed by a convergent lens with a focal length f and a plane mirror placed perpendicular to the principal axis of the lens, as shown in the figure.
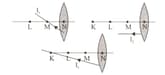
Accordingly, which of the rays have been given the correct path after the second time in the lens?
(Distance between points are equal and about f.)
