Process of Recombinant DNA Technology
Process of Recombinant DNA Technology: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Recombinant DNA Technology, Gel Electrophoresis, Restriction Enzymes, Bioreactors, Cloning Vectors, Downstream Processing, Electroporation, Microinjection, Plasmid as Vector and, Palindromic Nucleotide Sequence
Important Questions on Process of Recombinant DNA Technology
Choose the option that is showing the correct sequence of events occurring in each cycle of polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
A recombinant DNA is formed when sticky ends of vector DNA and foreign DNA join. The sticky ends are formed by which of the following enzymes:
Agrobacterium mediated genetic transformation described as natured genetic engineering is used to resist plants from:
Which of the following technique is used for separating the fragments of DNA cut by restriction endonucleases?
Biotechnologists refer to which of the following bacteria as a natural genetic engineer of plants.
Which of the following feature of a vector is required to identify the transformed cell?
In recombinant DNA technology, ‘molecular scissors’ are:
The source organisms that possess Taq polymerase are
An extra-chromosomal, self-replicating part of the cell that has proven to be a boon to biotechnology is:
In which of the following technique the bacterium Thermus aquatics is used:
Colonies of recombinant bacteria appear white in contrast to non-recombinant bacteria because of
The genes (a) ori, (b) ampR and (c) rop are associated with which of the following vectors:
Fragments of DNA segments can be separated by:
In genetic engineering, which of the following is used?
An experimenter ligated cDNA of p53 gene into the multiple cloning site (MSC) of a vector whose map is shown below. The ligated vector was transformed into E. coli cells, and transformants were initially selected on an agar plate containing antibiotic P. The bacterial colonies obtained on this plate were further propagated sequentially on antibiotic Q and then antibiotic R by replica plating.
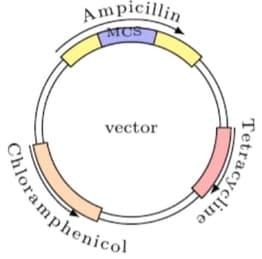
The correct sequence(s) of P, Q and R to be used to select E. coli colonies with p53 cDNA clones into MCS is/are:
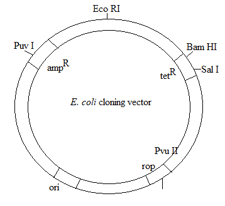
A gene is inserted into the Puv II site of the cloning vector (given below) and transformed into E. coli. Which one of the following statements is then true?
As opposed to DNA replication within the cell, discontinuous synthesis of DNA does NOT occur in a polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Why?
If recognition sequence of an enzyme has 4 bp, how many recognition sequences could you find in a DNA with 20 kb?
Which statement is incorrect?
There are important set of enzymes used in biotechnology. Match them with exact role:
| Column I | Column II | ||
| P | Taq DNA Polymerase | 1 | Cutting single stranded part of DNA |
| Q | S1 Nuclease | 2 | Ligase |
| R | Restriction Endonuclease | 3 | Thermostable enzyme |
| S | Molecular glue | 4 | Cutting palindromic sequence |
| 5 | Union of palindromic sequence |
