Ellingham Diagrams
Ellingham Diagrams: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Ellingham Diagram, Limitations of Ellingham Diagram and, Applications of Ellingham Diagram
Important Questions on Ellingham Diagrams
In the Ellingham diagram for the solid metals and , gaseous oxides and are:
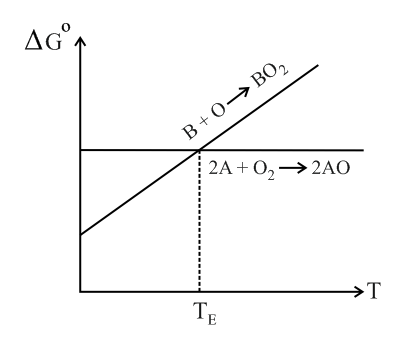
Below point can _____.
Which of the following metals cannot be obtained by reduction of its metal oxide by aluminium?
Ellingham diagram represents change of
Ellingham diagram is a graphical representation of :
Which one of the following statements is not correct?
Explain the reason due to which Ellingham diagram does not explain the kinetics of the reduction process.
Explain limitations of Ellingham diagram based on the kinetics of the reaction.
What are the limitations of Ellingham's diagram.
Considering Ellingham diagram, which of the following metals can be used to reduce alumina?
For a reaction
The free energy change is plotted as a function of temperature. The temperature below which the oxide is stable could be inferred from the plot as the point at which :
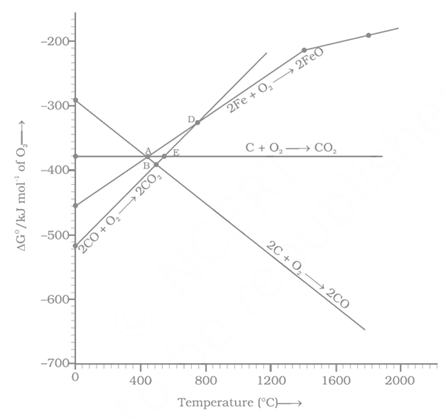
Carbon monoxide is more effective reducing agent than carbon below but above this temperature, the reverse is true –Explain.
Out of coke and , which is better reducing agent for the reduction of ? Why?
Explain the thermodynamic principle for the interpretation of the Ellingham diagram using haematite ore.
At which is the better reducing agent carbon or carbon monoxide?
What is the minimum temperature for reduction of by carbon?
Explain, how varies, with temperature in the reaction .
Which two parameters are plotted in Ellingham diagram.
Which of the following can act as strongest reducing agent below

Carbon cannot be used to produce magnesium and calcium by chemical reduction of MgO and CaO because:
