Theoretical Basis of Organic Reactions
Theoretical Basis of Organic Reactions: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as organic reactions and mechanisms, organic reactions, bond cleavage, homolytic bond cleavage, and conditions for homolytic bond cleavage.
Important Questions on Theoretical Basis of Organic Reactions
Correct order of rate hydrolysis or rate of reaction towards AgNO3 for following compounds is:
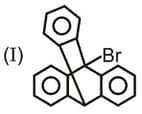
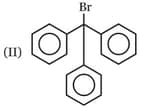
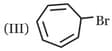
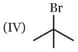
Write correct order of stability of following carbocations :
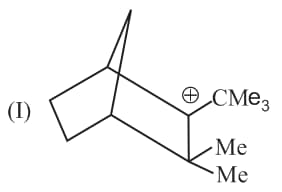
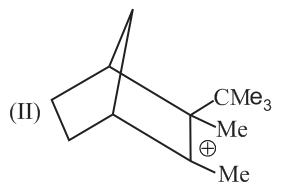
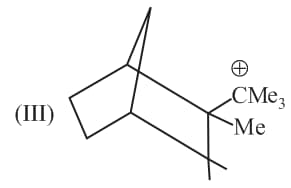
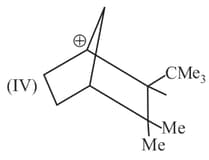
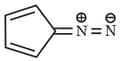
The most stable canonical structure of this molecule is:
In which of the following molecules / ions resonance structures are equivalent:
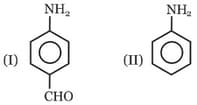
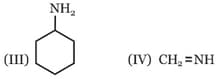
Among these compounds, the correct order of C–N bond length is :
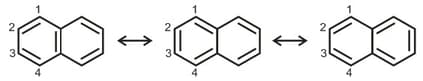
There are three canonical structures of naphthalene. Examine them and find the correct statement among the following:
Rank the following free radicals in order of decreasing stability:
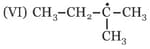
In which of the following pairs, is the first species is more stable than second?
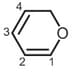
In this molecules, π-electron-density is more on
In which of the following molecules π-electron density in ring is maximum ?
In which of the following molecules π-electron density in ring is minimum ?
Which of the following compounds has maximum electron density in ring ?
Which of the following compounds has maximum electron density in ring ?
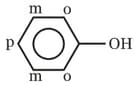
In phenol, π - electron - density is maximum on
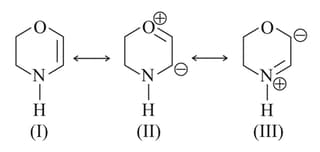
The least stable canonical structure among these is
The order of stability of these canonical forms is:
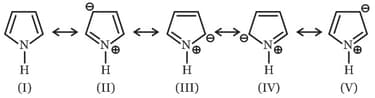
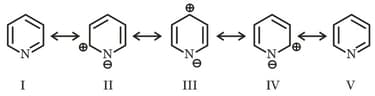
Among these canonical structures of pyridine, the correct order of stability is
The most stable resonating structure of following compound is
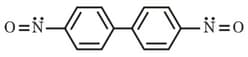
Among these three canonical structures (through more are possible) what would be their relative contribution in the hybrid?
is more stable than because
