Stereochemical Aspects of Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Stereochemical Aspects of Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Configuration, Racemic Mixture, Racemisation, Inversion of Configuration, Retention of Configuration, Chiral and Achiral, Dextrorotatory and Laevorotatory and, Molecular Asymmetry and Chirality
Important Questions on Stereochemical Aspects of Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Define relative configuration
If during a reaction, no bond to the stereocentre is broken, than the reaction will proceed with retention of the configuration.
The preservation of integrity of the spatial arrangement of bonds to an asymmetric centre during a chemical reaction is called inversion of configuration.
If during a reaction, the product has the same general configuration of groups around the stereocentre as that of reactant. Such a reaction is said to proceed with:
For a laevorotatory compound a negative () sign is placed before the degree of rotation.
A compound that rotates the plane polarised light in the anticlockwise direction, is said to be laevorotatory.
Explain the retention of configuration with an example.
Differentiate between dextrorotatory and laevorotatory compounds.
If the configuration of optically active remains unchanged during the reaction, it is called _____.
Define a laevorotatory compound.
Which of the following method is not used in the resolution of a racemic mixture?
Which of the following is taken as a reference to represent the relative configuration?
Which of the following compounds will give racemic mixture on nucleophilic substitution by ion? 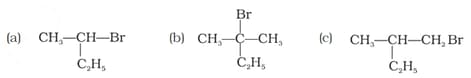
In case of optically active alkyl halides reactions are accompainied by _____ which results in zero rotation in polarimeter.
Write the enantiomeric forms of lactic acid. Assign each enantiomer with () or () designation.
Write the enantiomeric forms of glyceraldehyde. Assign each enantiomer with () or () designation.
Write the enantiomeric forms of Butan--ol. Assign each enantiomer with or designation.
Assume that your hands are equally strong and efficient, will you be able to do the following operation with same speed and efficiency?
Lifting a ball point pen.
Assume that your hands are equally strong and efficient, will you be able to do the following operation with same speed and efficiency?
Turning on water tap.
Assume that your hands are equally strong and efficient, will you be able to do the following operation with same speed and efficiency?
Cutting a piece of paper with scissor.
