Physical and chemical properties of alkyl halides
Physical and chemical properties of alkyl halides: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as physical properties of haloalkanes and haloarenes, colour of haloalkanes and haloarenes, chemical reactions of haloalkanes, reaction of haloalkanes with aqueous NaOH /aqueous NaOH, etc.
Important Questions on Physical and chemical properties of alkyl halides
Which of the following combinations amongst the four Fischer projections represents the same absolute configurations?
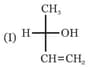
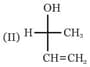
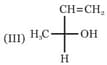
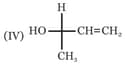
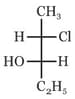
The compound with the above configuration is called:
Which of the following sugars has the configuration (2S, 3R, 4R)?
What kind of reagent would be needed to resolve a racemic amine, such as 2-aminobutane?
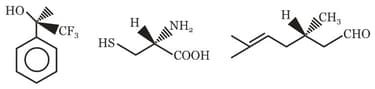
The R/S configuration of these compounds are respectively.
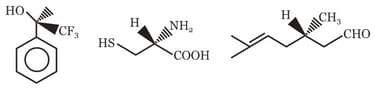
The R/S configuration of these compounds are respectively.
A pure simple of -chlorobutane shows rotation of PPL by in standard conditions. When above samples is made impure by mixing its opposite form, so that the composition of the mixture become -form and -form, then what will be the observed rotation for the mixture.
Identify A, B, C and D in the following process :
(i)
(ii)
A solution of (+) -2-chloro-2-phenylethane in toluene racemises slowly in the presence of small amount of , due to the formation of –
on treatment with produces –
on treatment with produces:
1–chlorobutane on reaction with alcoholic potash gives –
n–Propyl bromide on treatment with ethanolic potassium hydroxide produces –
The optically active tartaric acid is named as D-(+)-tartaric acid because it has a positive
In the reaction,
The product C is.
Explain the term 'stereocentre'.
Le Bel and Van't Hoff does not point out the following about carbon atom-
What causes the optical activity in lactic acid ?
Give the value of specific rotation of lactic acid.
Lactic acid form non-superimposable mirror image and exist as _____.
