Chain growth or addition polymerisation
Chain growth or addition polymerisation: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as free radical addition mechanism, reaction of chain initiation steps, and reaction of chain terminating step.
Important Questions on Chain growth or addition polymerisation
Briefly define the chain propagation step.
Disproportionation reaction forms saturated and unsaturated polymeric chain during chain termination step of addition polymerization.
The unsaturated polymer formed during termination of addition polymerization is known as living polymers.
What are disproportionation termination reaction? Give its reaction.
How chain propagation step is different from chain initiation step?
Why are the propagation steps described as a chain reaction?
State the chain propagating step in chlorination of methane.
Which of following will not be major product of the given below reaction:
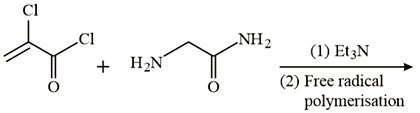
The major product of the following reaction is _________
Styrene
Write the name and structure of one of the common initiators used in free radical addition polymerisation.
Explain the chain termination mechanism of addition polymerisation reaction ?
The polymerisation of ethene to polythene consists of heating or exposing to light a mixture of ethene with a small amount of _____ initiator.
Give the detailed information about chain initiating step of polymerisation of ethene.
Write the steps involved in the free radical mechanism in polymerisation of ethylene.
Following monomer are used to prepare polymer. Predict the structure of polymer.
Isobutylene.
What are the different possibilities in the chain terminating step?
What is addition polymerisation? Explain free radical addition polymerisation mechanism by taking an example.
In free radical polymerization, what is the role of hydroquinone. Explain.
How many methods of chain termination are there in free radical mechanism?
What is not true regarding free radical polymerization of propene ?
