Electronic Effects
Electronic Effects: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Inductive Effect, Hyperconjugation, Mesomeric Effect, Electromeric Effects, Resonance Effect, Delocalised Electrons, Resonating Structures, Conditions for Resonance and, Acidic Strength of Organic Compounds
Important Questions on Electronic Effects
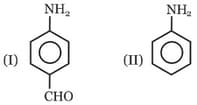
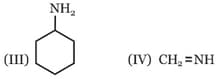
Among these compounds, the correct order of C–N bond length is :
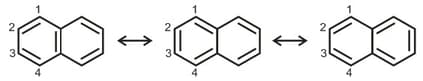
There are three canonical structures of naphthalene. Examine them and find the correct statement among the following:
In which of the following pairs, is the first species is more stable than second?
In which of the following molecules π-electron density in ring is maximum ?
In which of the following molecules π-electron density in ring is minimum ?
Which of the following compounds has maximum electron density in ring ?
Which of the following compounds has maximum electron density in ring ?
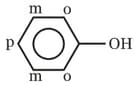
In phenol, π - electron - density is maximum on
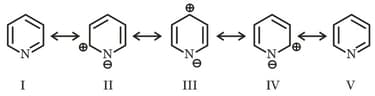
Among these canonical structures of pyridine, the correct order of stability is
In which of the following molecules - group is not coplanar with phenyl ring?
In which of the following molecules resonance takes place through out the entire system
The increasing order of basic strengths in their aqueous solutions is:
Hyperconjugation involves overlap of the following orbitals
Amongst the following, the most basic compound is
Which is more acidic: or ?
Explain the significance of mesomeric effect.
Why the carbon-carbon bond length is the same in benzene?
and groups shows -effect but shows effect. Why?
The reaction of ethene is the presence of can be example for -effect.
Which one of the following does not exhibit electromeric effect?
