Meter Bridge
Meter Bridge: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Meter Bridge etc.
Important Questions on Meter Bridge
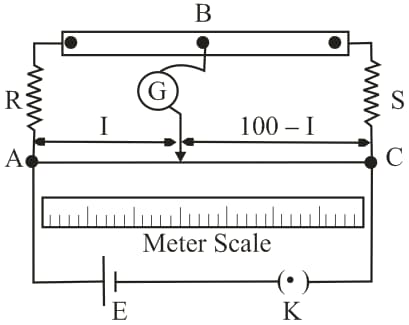
In a meter bridge balance point is found at a distance with resistances R and S as shown in the figure.
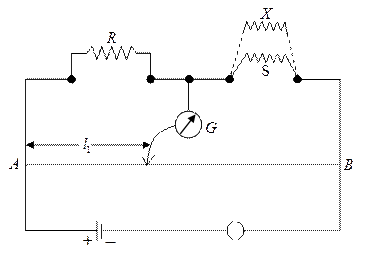
When an unknown resistance X is connected in parallel with the resistance S, the balance point shifts to a distance . Find the expression for X in terms of , and S.
Figure shows a Meter bridge wire has uniform cross-section. The length of wire is is a standard resistor of and is a coil. When is immersed in melting ice the null point is at from point . When the coil is heated to a resistor has to beconnected in parallel with in order to keep the bridge balanced at the same point. The temperature coefficient of resistance of the coil is units. Find the value of .
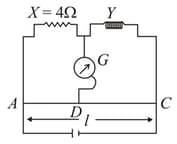
Consider the meter bridge circuit without neglecting end corrections. If we used and resistance in place of and respectively, we get null deflection at . If we interchange the resistances, the null deflection was found to be at . If and are the end correction, then the value of should be
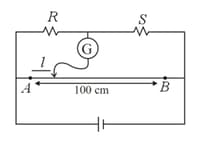
If the wire in the experiment to determine the resistivity of a material using metre bridge is replaced by copper or hollow wire the balance point i.e. null point shifts to
Null method is superior over deflection method because
Where do we get the balancing point of the meter bridge generally?
Two resistances and in the two gaps of a meter-bridge gives a null point dividing the wire in the ratio . If each resistance is increased by , the null point divides the wire in the ratio , choose the correct value of and .
Where do we get the balancing point of the meter bridge generally?
With resistance and in the left and the right gap respectively of a meter bridge, the null point divides the wire in the ratio . When and are increased by each, the mull point divides the wire in the ratio . Then the values of respectively are ___.____
In a meter bridge (as shown below), the null point is found at a distance of from If now a resistance of is connected in parallel with the null point occurs at from Determine the value of (in )
The figure shows a meter bridge wire having uniform cross-section. The length of wire is is a standard resistor of and is a coil. When is immersed in melting ice, the null point is at from point . When the coil is heated to , a resistor has to be connected in parallel with in order to keep the bridge balanced at the same point. The temperature coefficient of resistance of the coil is SI units. Find the value of .
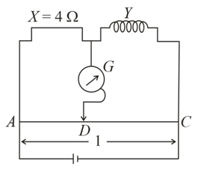
In a metre bridge experiment, null point is obtained at from one end of the wire when resistance is balanced against another resistance . If , then there will be the new position of the null point from the same end, if one decides to balance a resistance of against
In the following figure, a balanced meter bridge is shown. If the resistance of the wire of meter bridge is , then find the value of resistance X and the current passing through the resistance X.
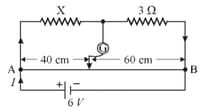
Two coils are connected in series in one gap of a meterbridge and the null point is obtained in the middle of the wire by putting in the other gap. Two coils are then connected in parallel and the null point is obtained again in the middle of the wire , the resistance in the other gap is changed by . Find the resistance of each coil.
With an unknown resistance in the left gap and a resistance of in the right gap of meter-bridge the null point is obtained at from the left end of the wire. Find the unknown resistance and the shift in the position of the null point
(a) when the resistance in both the gaps are increased by and
(b) when the resistance in each gap is shunted by a resistance of
The diagram shows a modified meter bridge, which is used for measuring two unknown resistances at the same time. When only the first galvanometer is used, for obtaining the balance point, it is found at point . Now, the first galvanometer is removed and the second galvanometer is used, which gives balance point at . Using the details given in the diagram, find out the values of and .
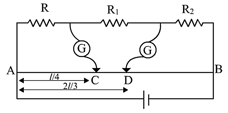
is a wire of potentiometer with the increase in the value of resistance , the shift in the balance point will be
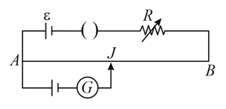
What is the value of unknown resistance , if galvanometer shows null deflection in the given meter bridge set up?
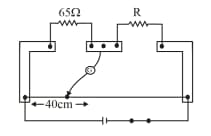
What happens to the balance point, When a metal conductor connected to left gap of a meter bridge is heated:
A resistance of 2 is connected across one gap of a meter-bridge (the length of the wire is 100 cm) and an unknown resistance, greater than 2 , is connected across the other gap. When these resistances are interchanged, the balance point shifts by 20 cm. Neglecting any end corrections, the unknown resistance is
