Electric Potential Due to a System of Charges
Electric Potential Due to a System of Charges: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Electric Potential due to a Charged Solid Sphere, Graph of Electric Potential Due to Charged Solid Sphere, Electric Potential due to a Charged Hollow Sphere and, Graph of Electric Potential Due to Charged Hollow Sphere
Important Questions on Electric Potential Due to a System of Charges
A charge is placed on a large spherical conducting shell of radius . Another small conducting sphere of radius r carrying charge is introduced inside the large shell and is placed at its centre. The potential difference between two points, one lying on the sphere and the other on the shell would be:
Two point charges are separated by a distance of 1m in air. Calculate at what point on the line joining the two charges is the electric potential zero.
A solid conducting sphere, having a charge is surrounded by an uncharged conducting hollow spherical shell. Let the potential difference between the surface of the solid sphere and that of the outer surface of the hollow shell be If the shell is now given a charge of the new potential difference between the same two surfaces is:
Two thin wire rings each having a radius are placed at a distance d apart with their axes coinciding. The charges on the two rings are and The potential difference between the centres of the two rings is :-
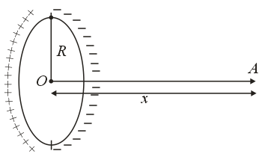
A charge is distributed over a thin ring of radius with line charge density . Note that the ring is in the -plane and is the angle made by with the -axis. The work done by the electric force in displacing a point charge from the centre of the ring to infinity is
A conducting sphere of radius is enclosed by a conducting shell whose radius of inner surface is and that of outer surface is . Charges given to conducting shell and conducting sphere are and respectively, then what will be potential at centre of conducting sphere :-
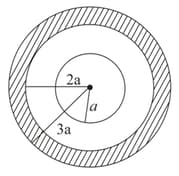
conducting spherical bubble of radius and thickness is charged to potential . If it collapses to form small spherical drop, then the potential of the drop is
Two identical rings each of radius are coaxially placed distance apart. They carry charges and respectively. If a charge is moved from the centre of one ring to the centre of the other ring, the work done is
Two identical thin rings, each of radius meters, are coaxially placed at a distance meters apart. If coulomb of charges is uniformly spread over both the rings, the work done in moving a charge from the centre of one ring to that of other is:
A spherical conductor of radius is charged to a potential of . It is now placed inside another hollow spherical conductor of radius Calculate the potential of bigger sphere, if the smaller sphere is made to touch the bigger sphere.
A charge Q is distributed over two concentric hollow spheres of radius r and R (< r) such that the surface densities are equal. The potential at the common centre is :
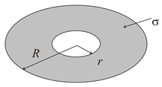
Figure shows a annular disc of outer radius inner radius and uniform surface charge density. Total charge is The potential at the centre is where is
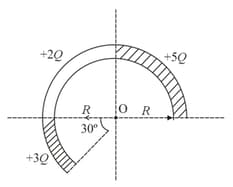
Three charges and are situated in plane at points and respectively. The potential in plane at a distant point in a direction making an angle from the Y-axis:-
An arc of radius is shown in the figure, find the potential at its centre:-
The radius of hollow metallic sphere is . If the potential difference between its surface and a point at a distance from its centre is then the electric field intensity at a distance of from its centre is:-
As one moves towards the centre from surface of uniformly charged metallic sphere the potential-
small water drops each of radius and charge coalesce together to form one spherical drop. The potential of the big drop is larger than that of the smaller drop by a factor of:-
A solid conducting sphere having a charge is surrounded by an uncharged concentric conducting hollow shperical shell. Let the potential difference between the surface of the solid sphere and that of the outer surface of the hollow shell be If the shell is now given a charge of the new potential difference between the same two surface is:-
Half of the non-conducting ring has charge and half has charge. Find potential at point which is on the line passing through centre perpendicular to plane of ring.
A charge is uniformly distributed through out the volume of a dielectric sphere of radius . If potential at its surface is volts. Then potential at and respectively are.... ...
(where distance from the centre of sphere):-
