Specific Heat Capacity
Specific Heat Capacity: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Specific Heat Capacity, Heat Capacity, Specific Heat Capacity of Water, Principle of Calorimetry, Heat Capacity of Solids, Molar Specific Heat Capacity and, Molar Specific Heat Capacity at Constant Pressure
Important Questions on Specific Heat Capacity
The molar heat capacity of water at constant pressure is . When 1kJ of heat is supplied to 100g of water, which is free to expand, the increase in temperature of water is
Derive the expression for .
A bullet of mass is fired with velocity and stop after hitting the target. Ifof its . goes increasing the temperature of the bullet then find raise in temperature (Specific heat capacity of bullet is )
A body of mass falls from a height of and rebounds to a height of . If the loss in energy goes into heating the body, then the rise in temperature will be nearly: (specific heat of material is )
Below is a graph between change in internal energy and temperature for a system placed in a constant volume.
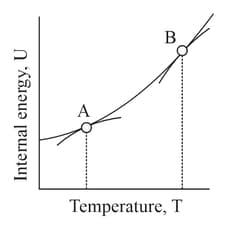
The slope of the graph is known as
Which one of the following material will expand maximum if the same amount of heat energy is given to them?
A block of specific heat capacity is heated with a heater of power at efficiency . Find the change in temperature if mass of the block is .
How much heat energy is necessary to raise the temperature of of ice from to steam at ?
The volume of moles of an ideal gas with degree of freedom is varied according to the law where is a constant. The molar specific heat of the gas at constant pressure is
Two identical systems, with heat capacity at constant volume that varies as (where is a constant) are thermally isolated. Initially, one system is at a temperature and the other is at . The systems are then brought to thermal contact and the combined system is allowed to reach thermal equilibrium. The final temperature (in ) of the combined system is . Write the value of where is the greatest integer function.
During an adiabatic process, the pressure of a gas is found to be proportional to the cube of its absolute temperature. The ratio for the gas is . Find .
The piston is massless and the spring is ideal and initially streched the piston cylinder arrangement encloses an ideal gas. If the gas is heated quasistatically the graph.
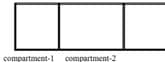
Figure shows a long fixed container which has two freely movable (without friction) pistons. The container and pistons are made of a thermally conducting material that allows very slow transfer of heat. First compartment of container is filled with moles of an ideal monoatomic gas at and the compartment is filled with mole of ideal diatomic gas at . Initially pressure of gases in both the compartment is same and equal to atmospheric pressure. Temperature of atmosphere is . Finally gases achieve equilibrium. '' is the gas constant
An ideal gas which undergoes through a process starting at and ends at . is a constant. The molar heat capacity of the gas if it is monoatomic is ; What is ?
The SI unit for heat capacity is joule per kelvin.
Define heat capacity with unit.
For a gas of molecular weight specific heat capacity at constant pressure is
Two litres of water at initial temperature of is heated by a heater of power in a kettle. If the lid of the kettle is open, then heat energy is lost at a constant rate of . The time in which the temperature will rise from to is,
(Specific heat of water )
Why the specific heat at a constant pressure is more than that at constant volume.
What are the two principal specific heats of a gas.
