Angular Momentum
Angular Momentum: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Angular Momentum of a Rigid Body in Pure Rotation, Angular Momentum and Angular Velocity, Angular Momentum & Angular Momentum of Particle about a Fixed Point etc.
Important Questions on Angular Momentum
A planet of mass is in an elliptical orbit about the sun with an orbital period . If be the area of orbit, then its angular momentum would be
Consider a particle of unit mass being thrown with an initial velocity making an angle with the horizontal ground. What is the magnitude of the angular momentum of the particle about the point of projection at a time after its projection while it is in fight?
Particles of mass and initially sitting at the same position, start moving simultaneously at with velocities and , respectively. After a time the angular momentum of the particle of mass with respect to the particle of mass is
A planet of mass moves in an elliptical path around the Sun (which is at one of the foci of the ellipse), so that its maximum and minimum distances from the Sun are and , respectively. Taking the gravitational constant to be and the mass of the Sun to be , what is the angular momentum of the planet relative to the centre of the Sun?
A bob of mass m attached to an inextensible string of length is suspended from a vertical support. The bob rotates in a horizontal circle with an angular speed rad/s about the vertical. About the point of suspension :
Which of the following physical quantity is represented by the product of the moment of inertia and angular velocity?
A ball of mass is thrown up at an angle of to the horizontal at a speed of . The angular momentum of the ball at the highest point of the trajectory with respect to the point from which the ball is thrown is nearly
An object of mass is projected from ground, with initial velocity , making angle with the horizontal. Find its angular momentum about the point of projection when the object is at its maximum height. (Take )
A particle of mass starts from rest at from a point and gets accelerated at along in plane. The angular momentum of the particle about the origin (in SI units ) at is
Assertion : The net momentum of a system of two moving particles is zero. Then at a particular instant of time, the net angular momentum of system of given two particle is same about any point.
Reason : If net momentum of a system of two moving particle is zero, then angular momentum of system of given two particles is zero about any point.
An object of mass is projected from ground, with initial velocity , making angle with the horizontal. Find its angular momentum about the point of projection when the object is at its maximum height. (Take )
A ball of mass is thrown directly upward from axis from position. The initial speed of the ball is The magnitude (absolute value) of the angular momentum of the ball about the origin when the ball is halfway back to the ground is:
An object of mass is moving with a uniform velocity of parallel to the direction. At the time of s the particle is located on the axis meters away from the origin then the angular momentum (in ) about at is
A bullet of mass and speed is fired horizontally into a door and gets embedded exactly at the centre of the door. The door is wide and weighs It is hinged at one end and rotates about a vertical axis practically without friction. The angular speed of the door just after the bullet embeds into it will be nearly
A mass is moving with a constant velocity along a line parallel to -axis. Its angular momentum with respect to origin or -axis is
A particle is moving on circular path with decreasing speed. Select the correct statement.
I. Angular momentum about centre of path remains constant.
II. Linear momentum remains constant.
III. The direction of angular momentum about centre of path remains constant.
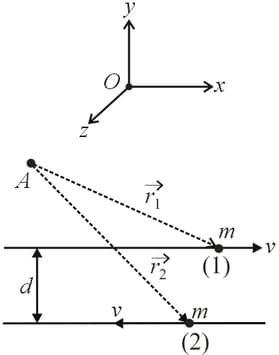
Figure given shows two identical particles and each of mass moving in opposite directions with same speed along parallel lines. At a particular instant, and are their respective position vectors drawn from point which is in the plane of the parallel lines. Then
If a particle moves in the plane, the angular momentum about origin has,
A rod of mass and length is lying along the Y axis such that one of its end is at the origin. An Impulse is given to the rod due to which its end at origin acquire a velocity of and other end acquires a velocity . What is magnitude of angular momentum of rod about origin.
