Linear Momentum of a System of Particles
Linear Momentum of a System of Particles: Overview
This topic consists of various concepts like Linear Momentum,Linear Momentum and Kinetic Energy in System of Particles,Linear Momentum of System of Particles, etc.
Important Questions on Linear Momentum of a System of Particles
An object of mass and another object of mass are moving such that they have equal kinetic energy. The ratio of the magnitudes of their linear momentum is
A body of mass 5 kg explodes at rest into three fragments with masses in the ratio 1 : 1 : 3. The fragment with equal masses fly in mutually perpendicular directions with speeds of 21 ms-1. The velocity of heaviest fragment in ms-1 will be
A shell is fired from a canon, it explodes in mid air, its total :
A particle of mass m is projected towards a wall such that the angle of incidence is 0 and the speed just before collision is. Assuming that the wall is smooth and the collision is elastic, show that the ball rebounds at same angle.
A railway wagon (open at the top) of mass is moving with speed along a straight track. As a result of rain, after some time it gets partially filled with water so that the mass of the wagon becomes and speed becomes . Taking the rain to be falling vertically and water stationary inside the wagon, the relation between the two speeds and is :
A nucleus disintegrates into two nuclear parts, in such a way that ratio of their nuclear sizes is . Their respective speed have a ratio of . The value of is_________
A particle of mass moving with velocity collides with a stationary particle of mass . After collision, they stick together and continue to move together with velocity
A bullet of mass moving horizontally with speed hits a wooden block of mass kept on a horizontal rough surface. The bullet gets embedded into the block and moves before coming to rest. The coefficient of friction between the block and the surface is _______.
A particle of mass moving with a velocity collides with a particle of mass at rest and sticks to it. Velocity of combined mass is equal to
A sphere of mass falls on a smooth hemisphere of massresting with its plane face on smooth horizontal table, so that at the moment of impact, line joining the centres makes an angle with the vertical. The velocity of sphere just before impact isand is the coefficient of restitution.
A ball of mass strikes the fixed inclined plane after falling through a height. If it rebounds elastically, the impulse on the ball is:
A man of mass stands on a long flat car of mass moving with velocity . If he now begins to run with velocity with respect to the car, in the same direction as the velocity of the car will be:
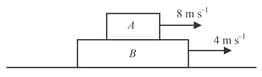
Block of mass is placed on the rough surface of block of mass . Block B is placed on smooth horizontal surface. Blocks are given the velocities as shown. Find net work done by the frictional force. [in ]
A body at rest breaks up into 3 parts. If 2 parts having equal masses fly off perpendicularly each after with a velocity of , then the velocity of the third part which has 3 times mass of each part is
Two bodies of masses and are dropped from heights and respectively. On reaching the ground, they acquire equal momenta. If , the ratio of kinetic energy of to that of on reaching the ground will be
Two balls A and B having mass and , moving with speed and respectively in opposite direction, collide head on. After collision A moves with a speed of in the same direction, then the coefficient of restitution is:
Two particlesand of equal masses having initial velocitiesand respectively collide. collision is head-on and elastic, then the final velocities of and respectively will be
Compare the momentum of two of this of mass and respectively but having the same kinetic energy.
A flat car of mass is at rest on a frictionless floor with a child of mass m standing at the edge. If the child jumps off from the car towards right with initial velocity , with respect to car, find the velocity of car after the jump.
A bomb moving with velocity explodes into two pieces of mass ratio . After explosion the smaller piece moves away with velocity . The velocity of the larger piece is
