Huygen's Principle
Huygen's Principle: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Quantum Theory of Light, Wave Theory of Light, Newtons Corpuscular Theory, Spherical Wavefront, Plane Wavefront, Cylindrical Wavefront, Secondary Wavelets, Dual Nature of Electromagnetic Radiation and, Wavefront and Ray
Important Questions on Huygen's Principle
Describe a wavefront and its different types .
What is Huygens wave principle?
The optical path of monochromatic light's the same if it travels thickness of glass or thickness of water. If the refractive index refractive is what is the refractive index of glass?
The interfering fringes forward by a thin oil film on water are seen in yellow light of sodium lamp. We find the fringes
The fringe width for red colour as compared to that for violet colour is approximately
If two coherent sources are vitro ting in phase then we have constructive interference of any point whenever the path difference is
Huygens wave theory of light can not explain-
Light propagates rectilinearly due to-
Two coherent monochromatic light beams of intensities and superimpose. The maximum and minimum possible intensities in the resulting beam are;
When light suffers reflection at the interface between water and glass, the change of phase on the reflected wave is
A plane wave passed through a convex lens. The geometrical shape of the wavefront that emergens is
According to Huygens' principle, light is a from of
When a piece of metal is illuminated by a monochromatic light of wavelength ,then stopping potential is , when same surface is illuminated by light of wavelength ,then stopping potential becomes . The value of threshold wavelength for photoelectric emmision will be-
Let be the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons emitted by light of wavelength and corresponding to wavelength . If , then
When a proton is accelerated through , then it kinetic energy will be .
What will be the photon energy for a wavelength of . If the energy of a photon corresponding to a wavelength of is ?
Fine rectangular slit is an example of _____ wavefront.
Light waves travel in vacuum along the -axis. Which of the following may represent the wavefront?
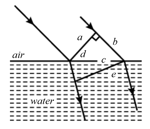
Figure shows plane waves refracted from air to water using Huygens' principle and , , , , are lengths on the diagram. The refractive index of water with respect to air is in the ratio