Structure of a Bisexual Flower
Structure of a Bisexual Flower: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Stamen, Carpels, Sepal, Bisexual Flower, Bract, Hypogynous Flowers, Petals of a Flower, Perigynous Flowers, Epigynous Flowers, Accessory Whorls of a Flower and, Essential Whorls of a Flower
Important Questions on Structure of a Bisexual Flower
Epigynous flowers are present in
Rose is an example of epigynous flower.
The flowers in which gynoecium stays in the centre and other parts of the flower are located on the rim of the thalamus is called _____ flower
Perigynous flowers are found in which plant?
Rose is an example of perigynous flower.
In a _____ flower, the ovary occupies the highest position on the thalamus.
When the petals of a flower are free, they are called _____ flowers.
The _____ connects the stigma to the ovary.
The _____ forming the calyx protect the young flower buds.
The essential parts of the flower include _____ and carpels making up the androecium and gynoecium respectively.
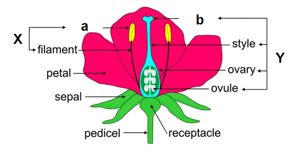
'b' along with the style and ovary are parts of X. All the 'X' in a flower are collectively called the gynoecium. What is 'b' in the given diagram?
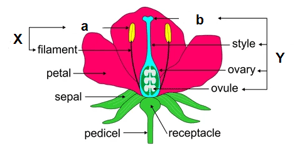
'a' and the filament are the two parts of X. All the 'X' in a flower are collectively called androecium. What is 'a' in the given diagram?
Which of the following terms is/ are related to the second whorl of the flower?
Which of the following terms is/ are related to the first whorl of the flower?
Which of the following is/are accessory whorls of a flower?
Which of the following is/are the essential whorls of a bisexual flower?
Petals of jasmine and rose look similar.
The colourful parts of the flowers are called
