From Flowers to Fruits and Seeds
From Flowers to Fruits and Seeds: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Fruits, Dry Fruits, Seed, Zygote, Seed Germination, Endosperm, Seed Dispersal, Plumule, False Fruit, Radicle, Parthenocarpic Fruit, Epigeal Germination, Hypogeal Germination, Structure of a Dicot Seed and, Fleshy Fruits
Important Questions on From Flowers to Fruits and Seeds
Are maize and wheat examples of monocotyledonous plants?
Fill in the blank by unscrambling the word given below.
DISBR
_____may disperse seeds, by carrying them on their beaks after feeding.
Name two birds disperse seeds.
How do birds disperse seeds?
Which among the following is incorrect about structure in a monocotyledon seed?
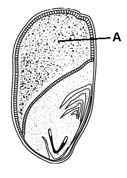
Identify the labelled 'A' from the monocot seed given below.
Examples of epigeal germination include
In epigeal germination, the epicotyl elongates and the cotyledons remain below the soil.
Give two examples of hypogeal germination.
Explain the temperature is necessary for seed germination.
Draw a labelled diagram of the structure of the monocot seed.
Explain air is necessary for seed germination.
Define parthenocarpic fruit.
Write down the essential elements or factors required for the germination of seed.
Write down the essential elements for seed germination.
Choose the true fruit.
What are true fruits?
Apple fruit is called pome because its pericarp is
Name the different types of fleshy fruits.
Which of the following is the fleshy fruit?
